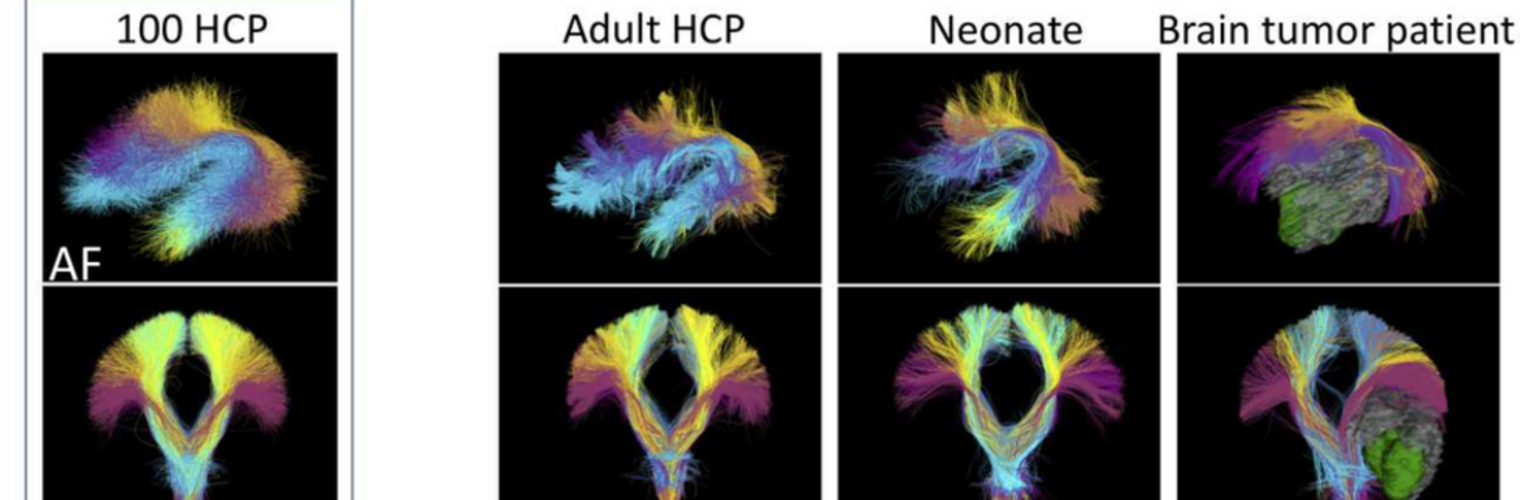
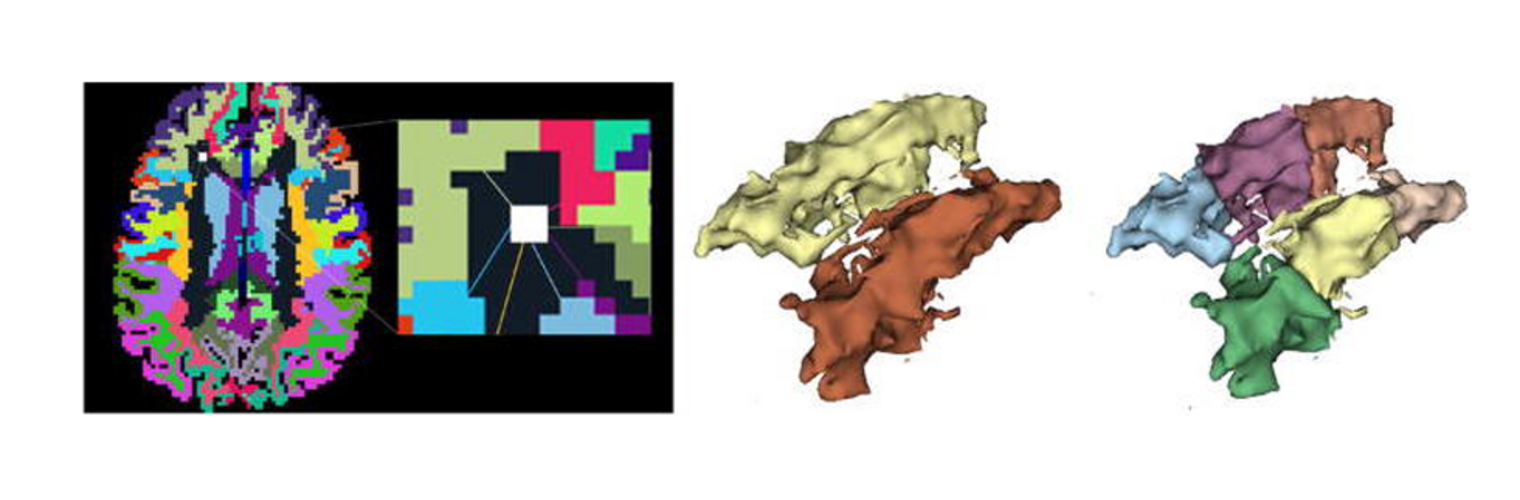
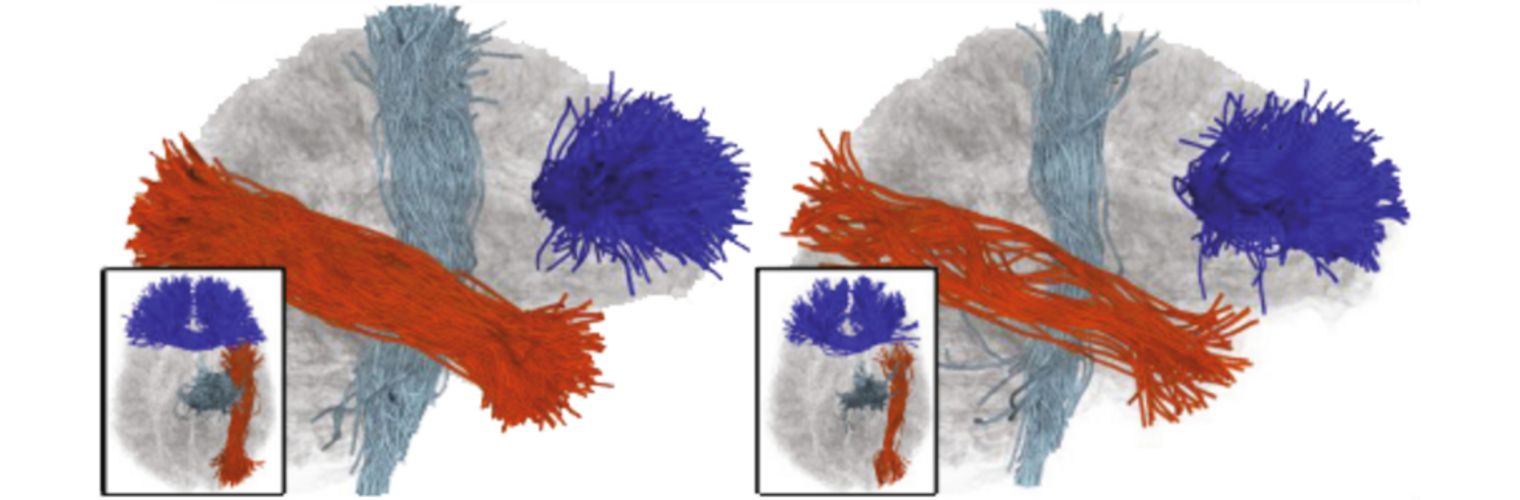
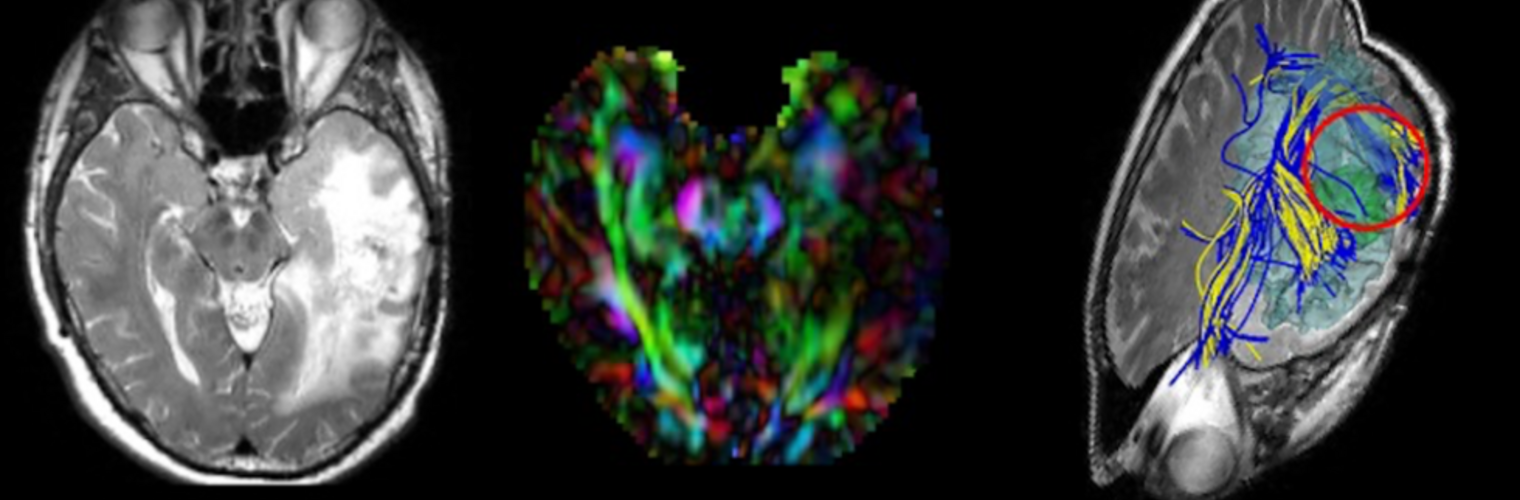
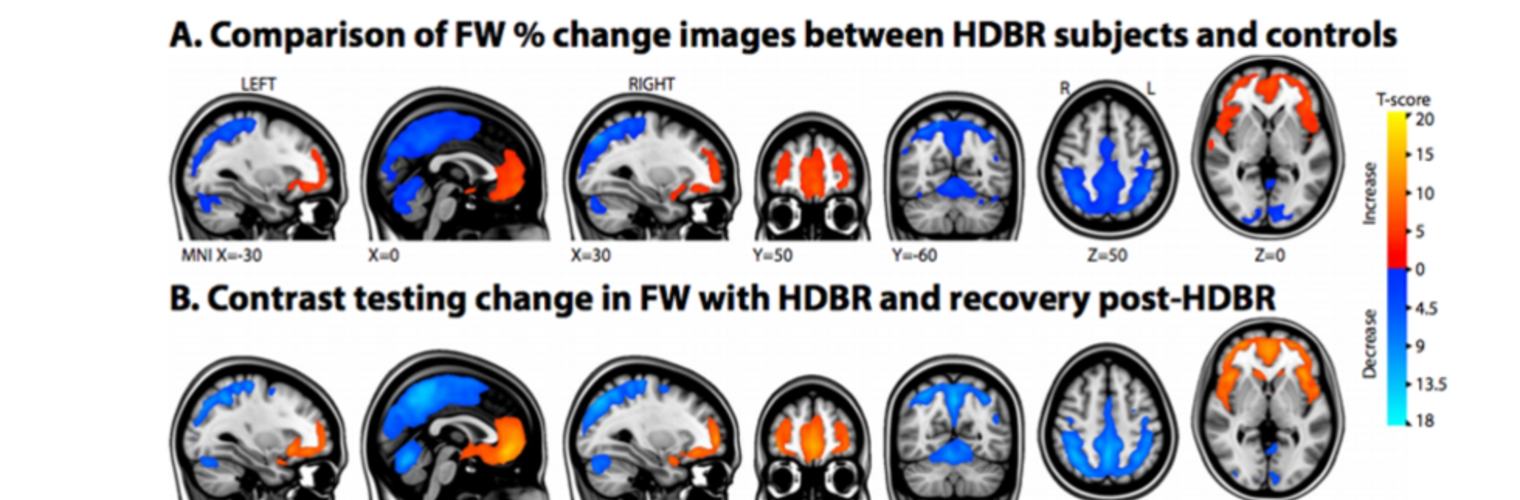
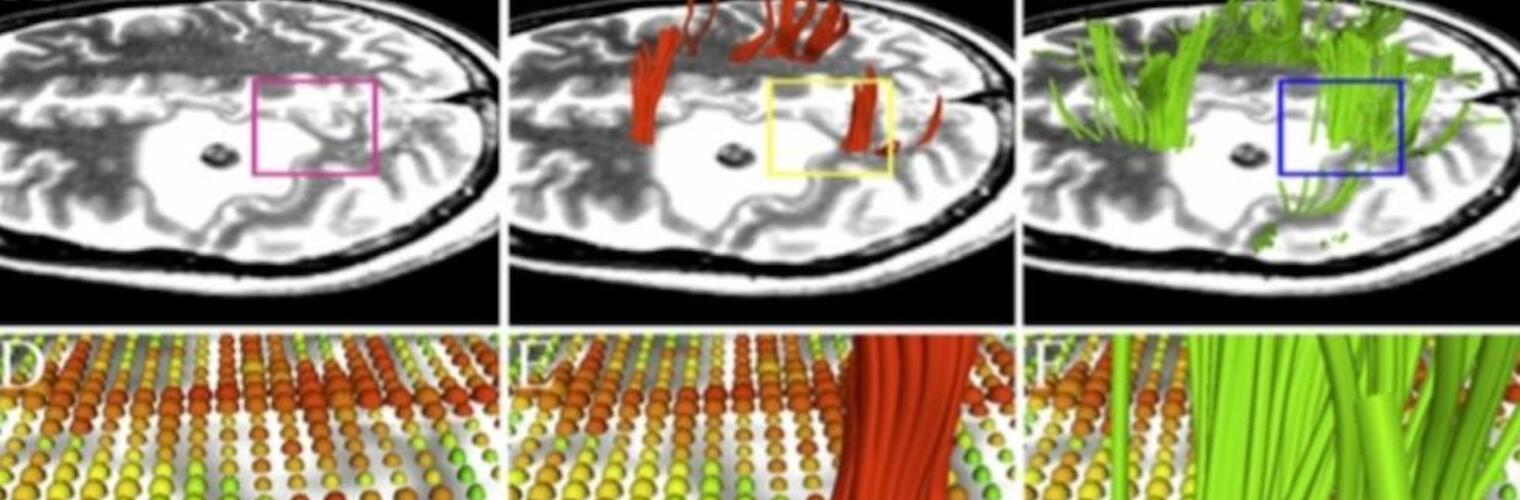
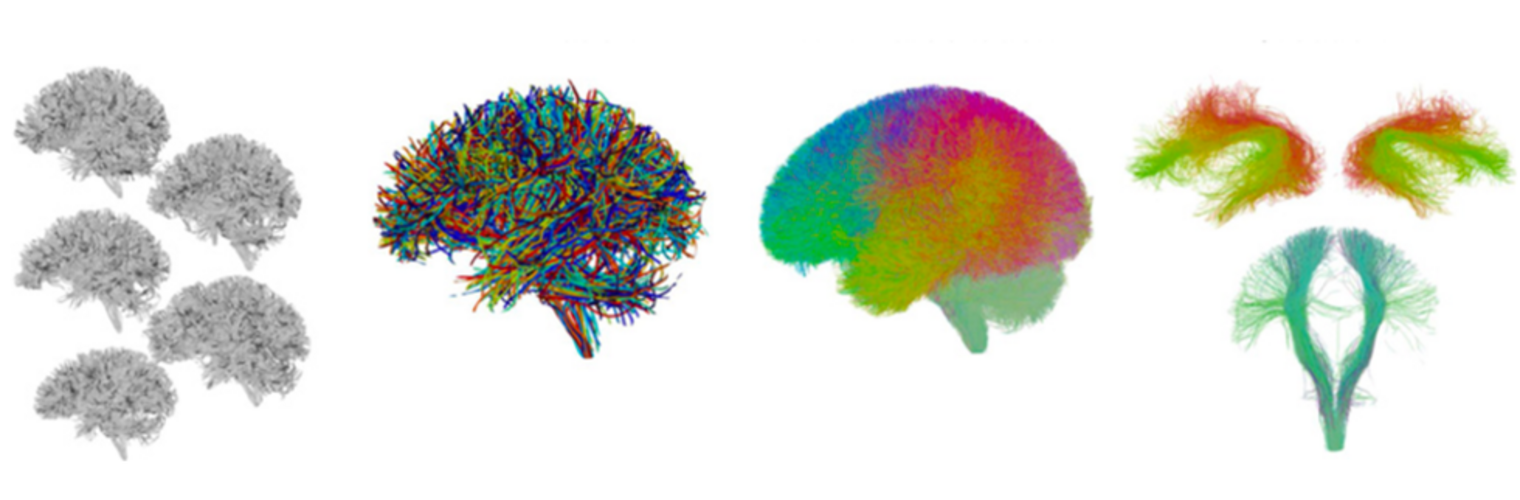
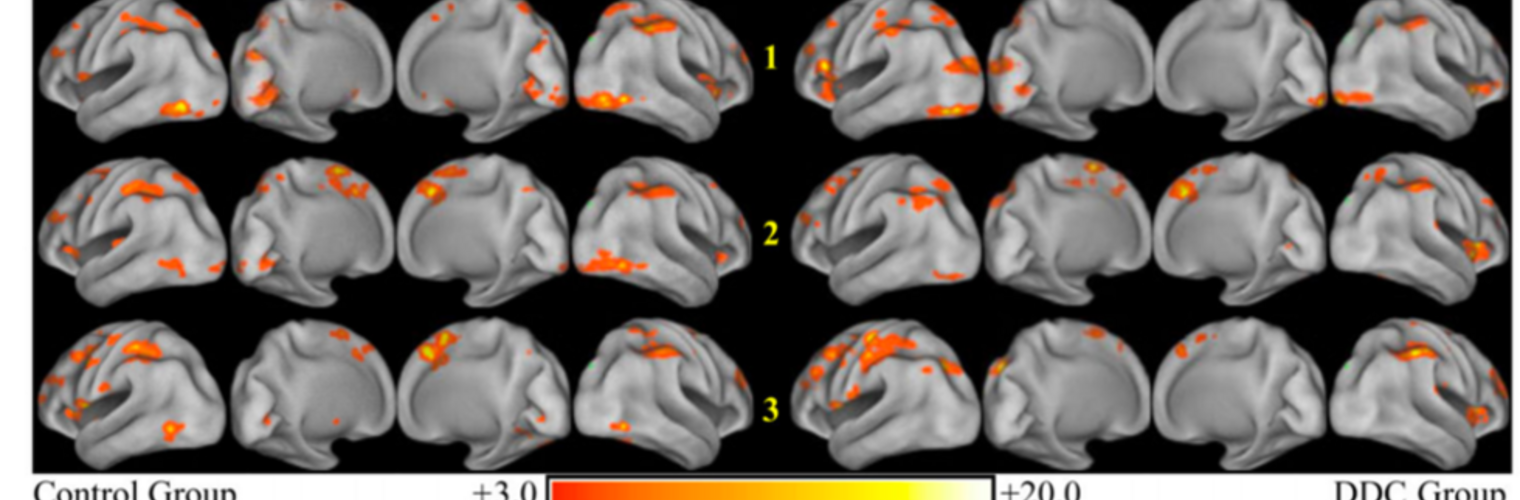
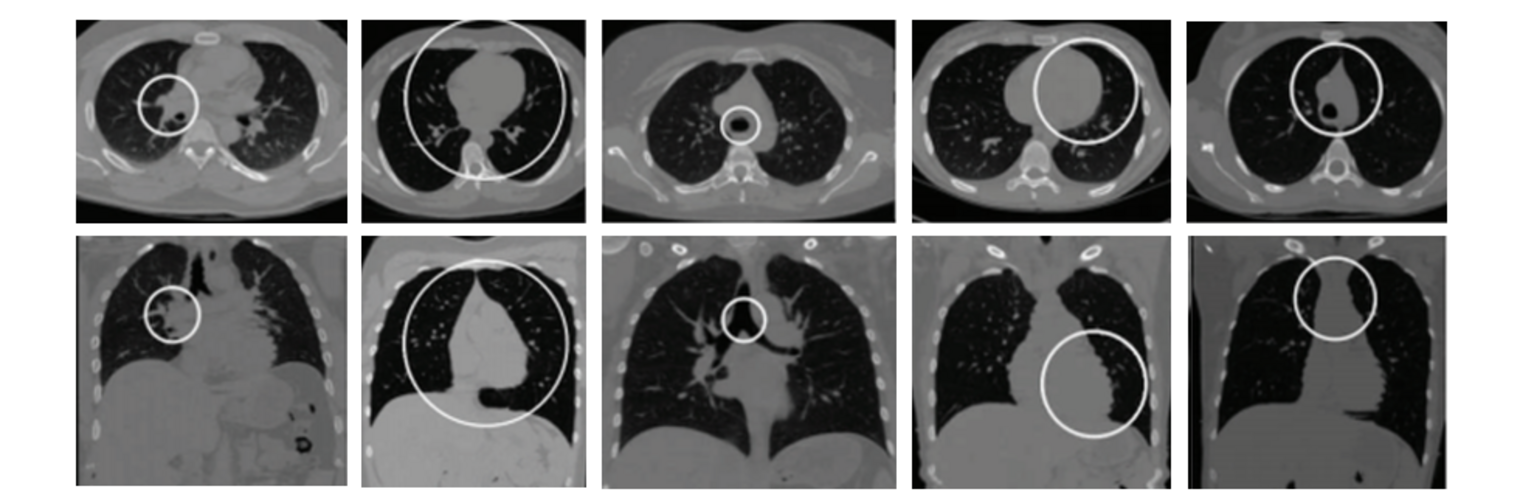
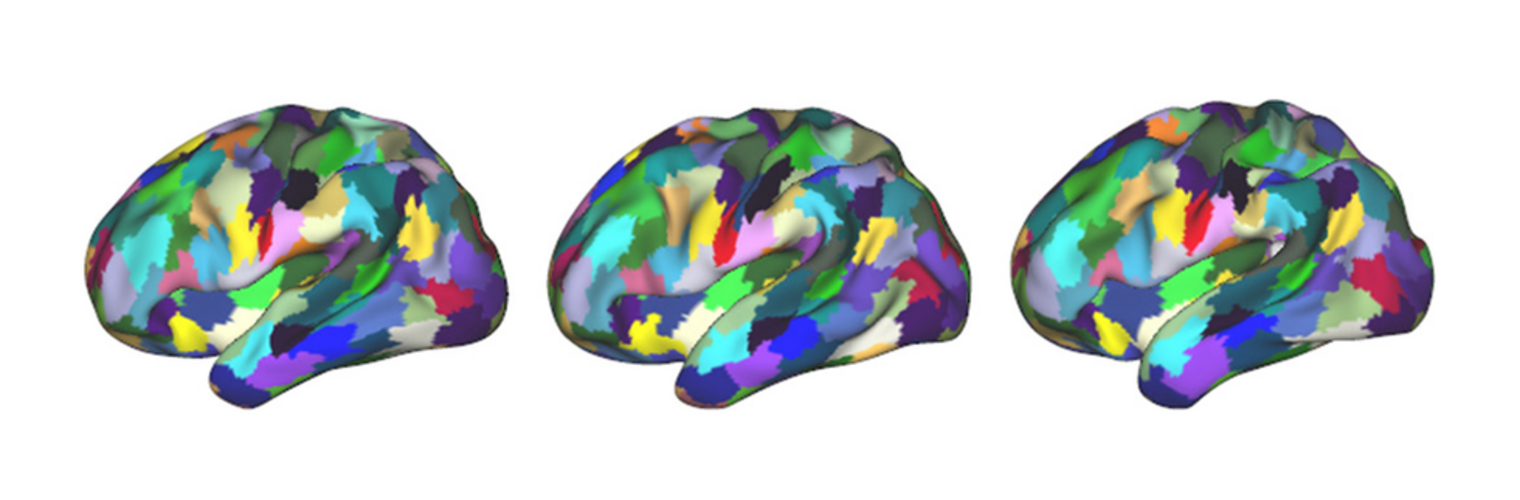
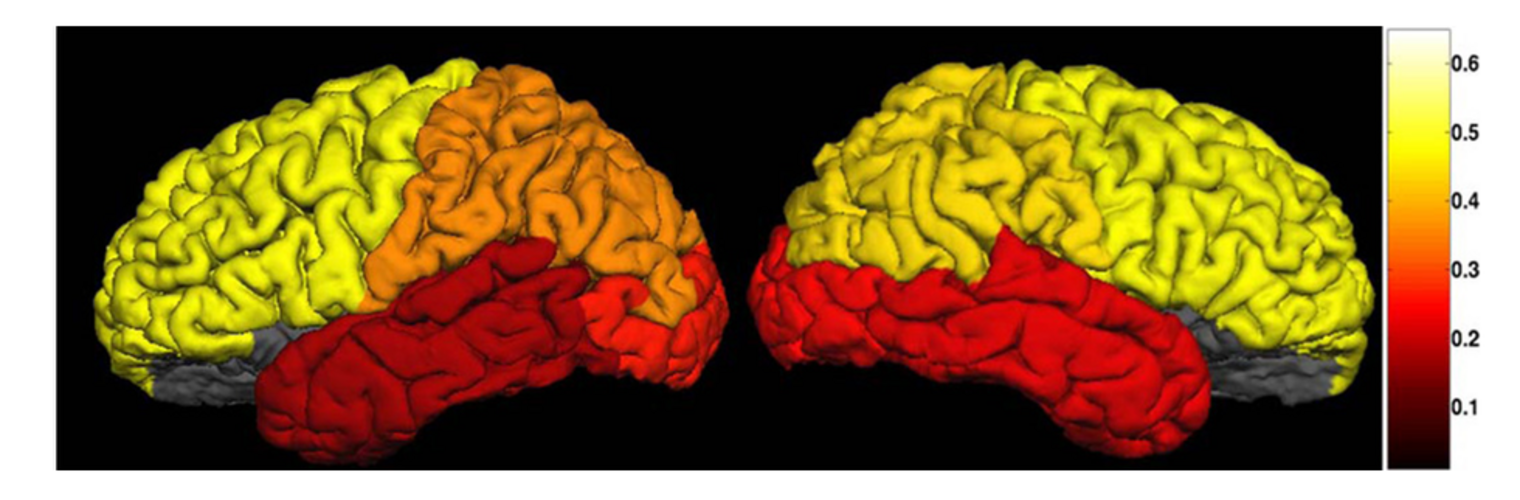
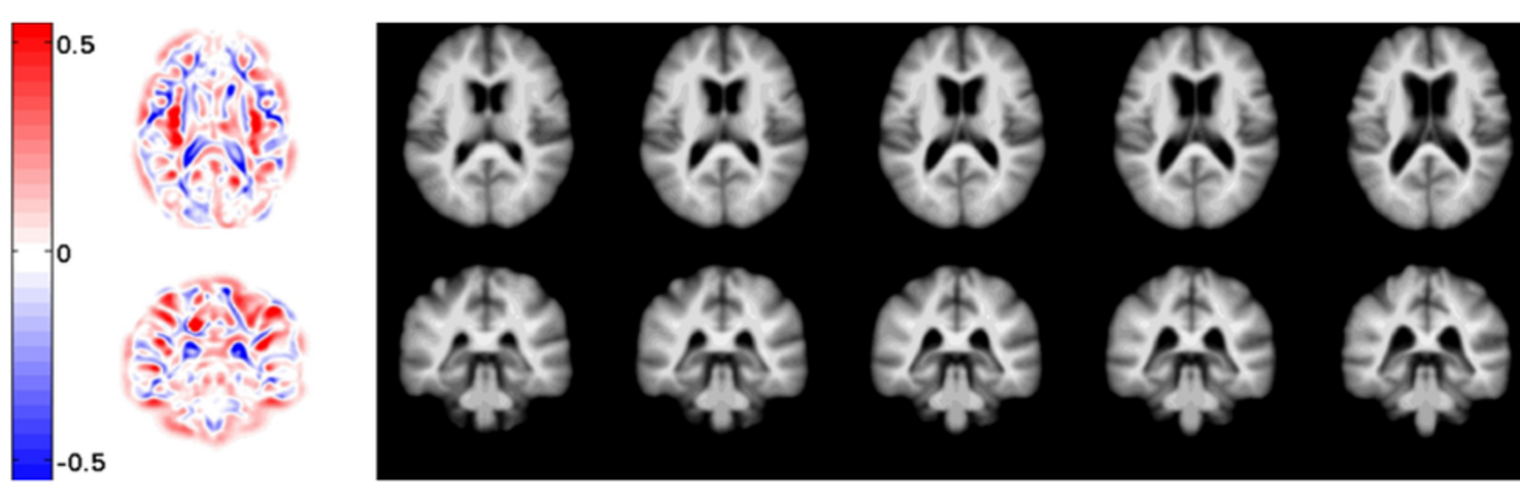
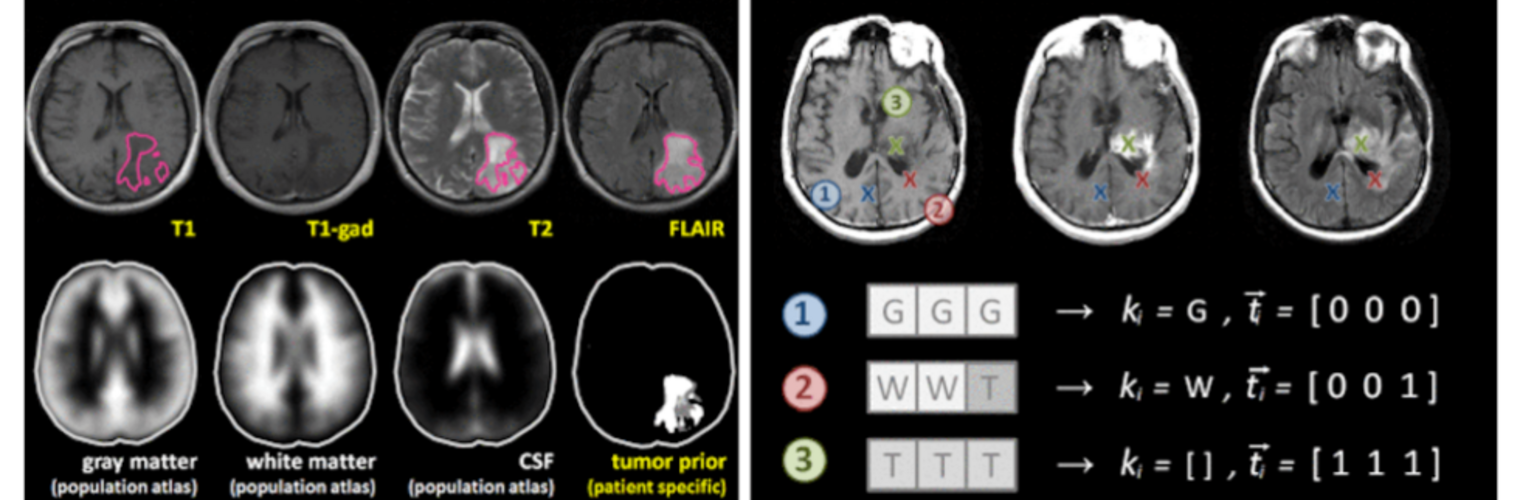
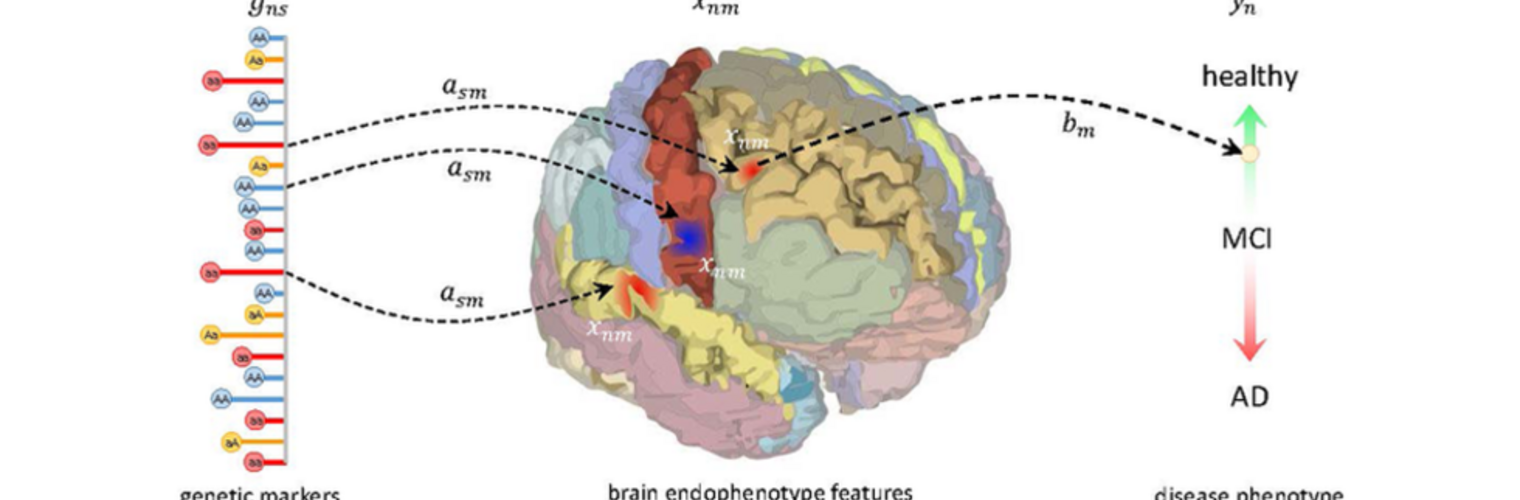
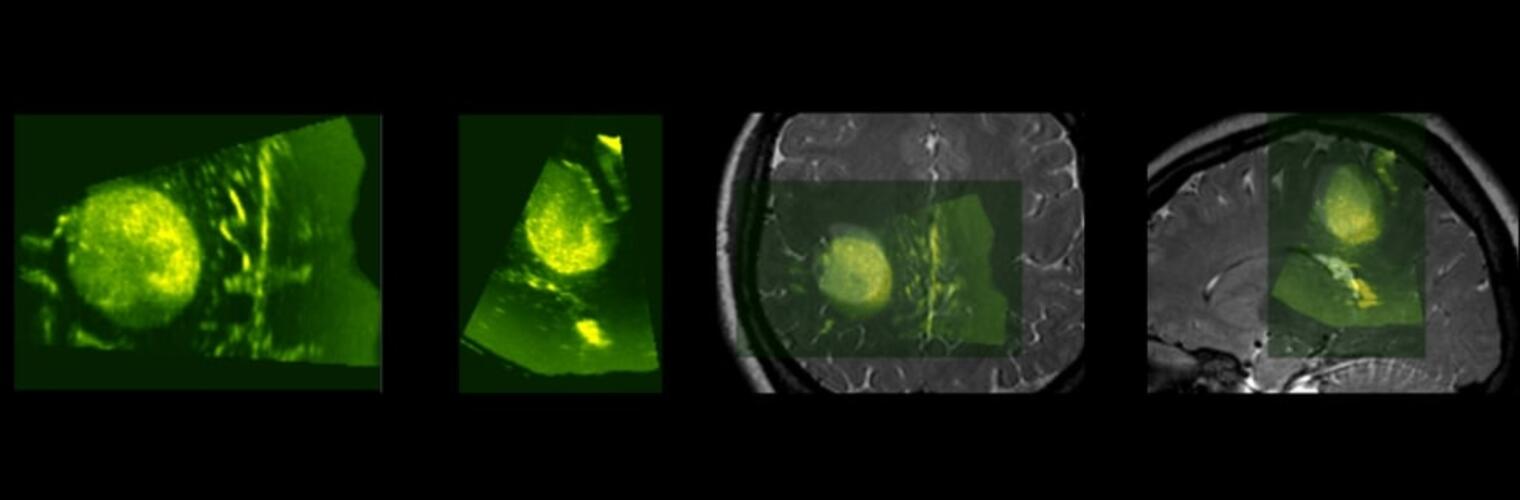
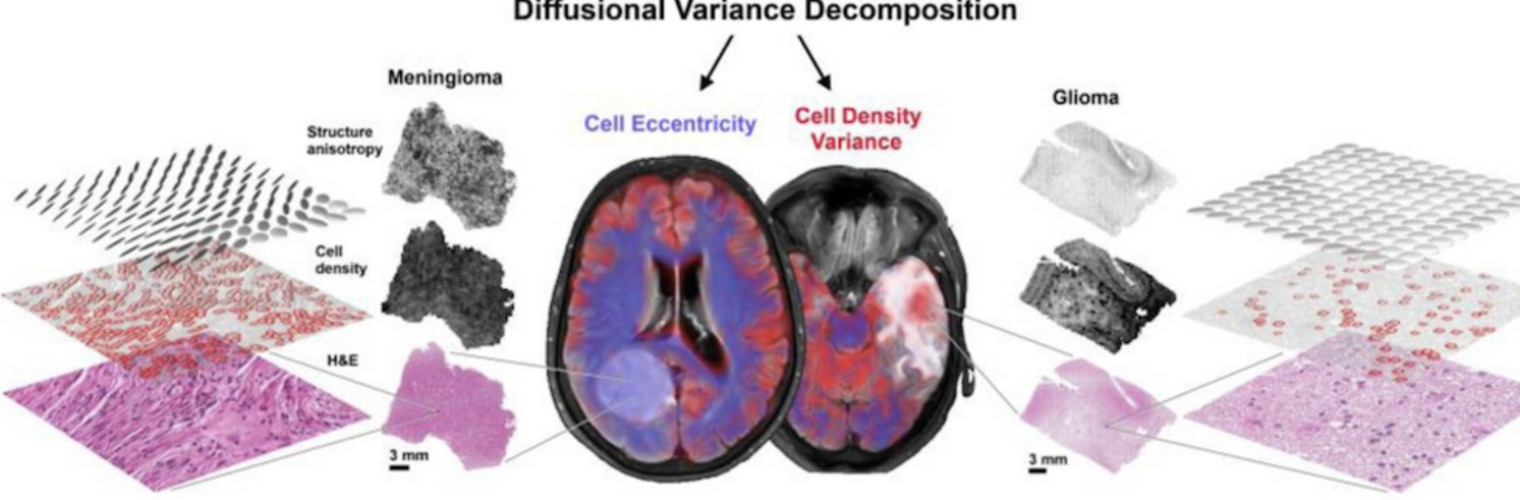
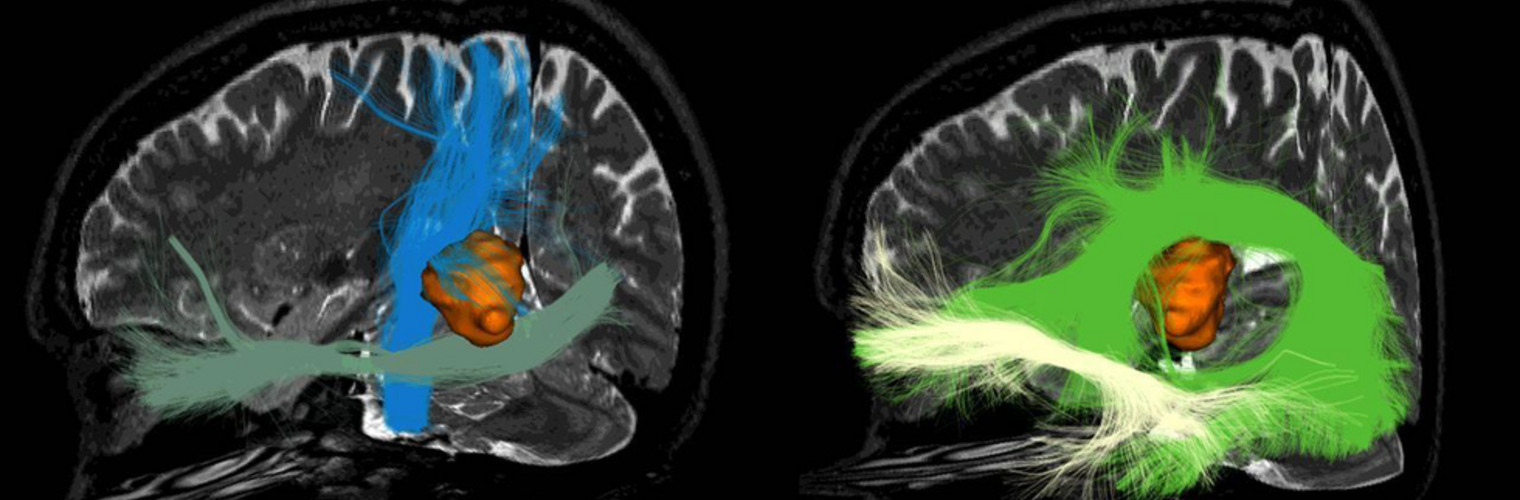
Diffusion MRI tractography is an advanced imaging technique that enables in vivo mapping of the brain's white matter connections. White matter parcellation classifies tractography streamlines into clusters or anatomically meaningful tracts. It enables quantification and visualization of whole-brain tractography. Currently, most parcellation methods focus on the deep white matter (DWM), whereas fewer methods address the superficial white matter (SWM) due to its complexity. We propose a novel two-stage deep-learning-based framework, Superficial White Matter Analysis (SupWMA), that performs an efficient and consistent parcellation of 198 SWM clusters from whole-brain tractography. A point-cloud-based network is adapted to our SWM parcellation task, and supervised contrastive learning enables more discriminative representations between plausible streamlines and outliers for SWM. We train our model on a large-scale tractography dataset including streamline samples from labeled long- and medium-range (over 40 mm) SWM clusters and anatomically implausible streamline samples, and we perform testing on six independently acquired datasets of different ages and health conditions (including neonates and patients with space-occupying brain tumors). Compared to several state-of-the-art methods, SupWMA obtains highly consistent and accurate SWM parcellation results on all datasets, showing good generalization across the lifespan in health and disease. In addition, the computational speed of SupWMA is much faster than other methods.
Neuroimage Analysis Center
The Neuroimaging Analysis Center is a research and technology center with the mission of advancing the role of neuroimaging in health care. The ability to access huge cohorts of patient medical records and radiology data, the emergence of ever-more detailed imaging modalities, and the availability of unprecedented computer processing power marks the possibility for a new era in neuroimaging, disease understanding, and patient treatment. We are excited to present a national resource center with the goal of finding new ways of extracting disease characteristics from advanced imaging and computation, and to make these methods available to the larger medical community through a proven methodology of world-class research, open-source software, and extensive collaboration.
Our Sponsor

The NAC is a Biomedical Technology Resource Center supported by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) (P41 EB015902). It was supported by the National Center for Research Resources (NCRR) (P41 RR13218) through December 2011.
Contact the Center Directors
|
|
Carl-Fredrik Westin, PhD Laboratory of Mathematics in Imaging Brigham and Women's Hospital 1249 Boylston St., Room 240 Boston, MA 02215 Phone: +1 617 525-6209 E-mail: westin at bwh.harvard.edu |
|
|
|
Ron Kikinis, MD Surgical Planning Laboratory Brigham and Women's Hospital 75 Francis St, L1 Room 050 Boston, MA 02115 Phone: +1 617 732-7389 E-mail: kikinis at bwh.harvard.edu |