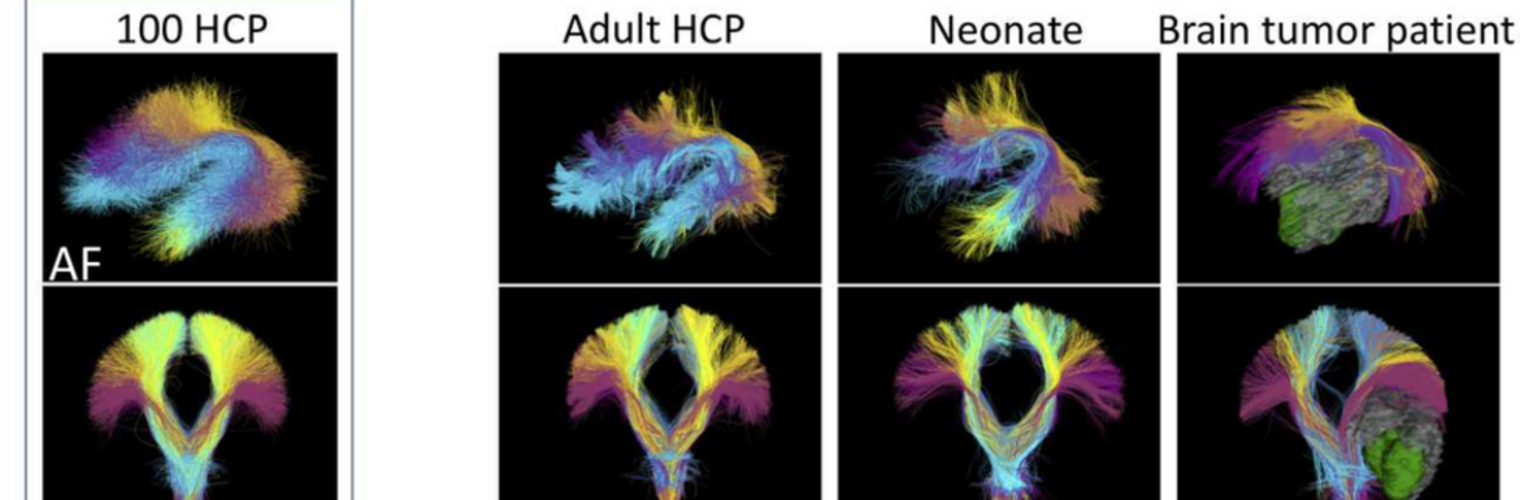
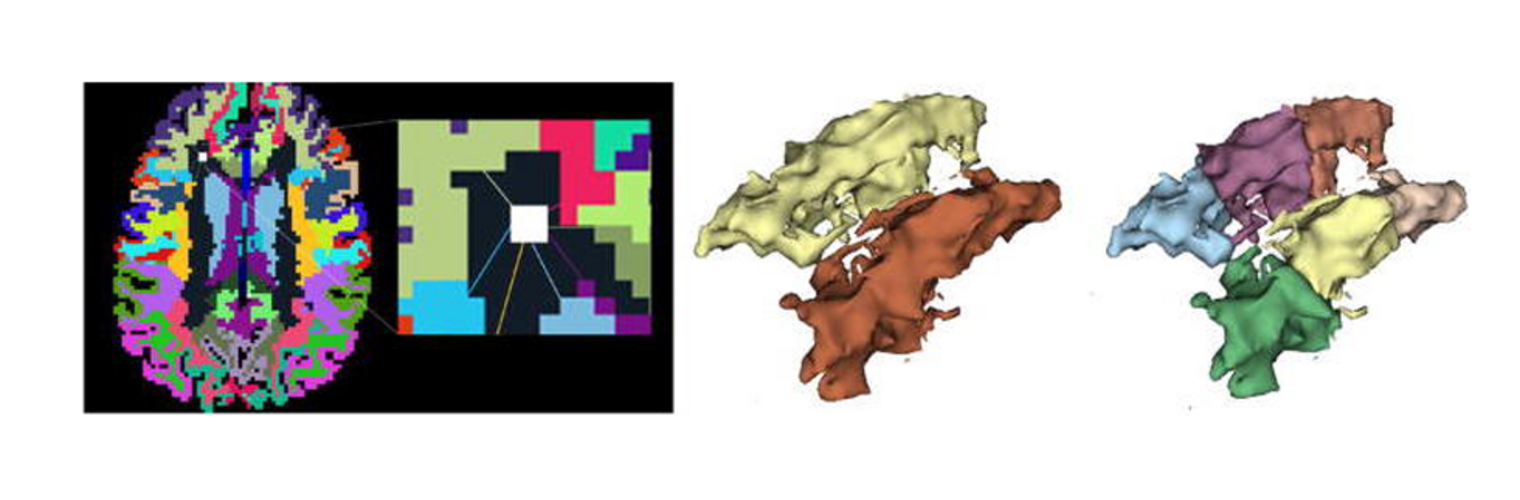
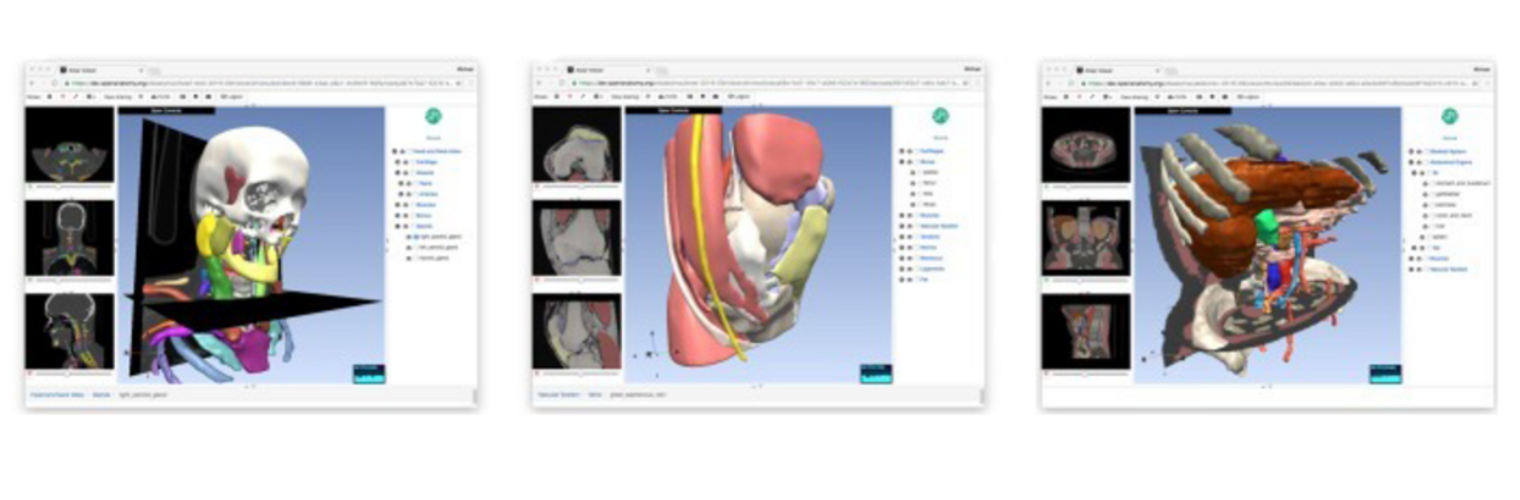
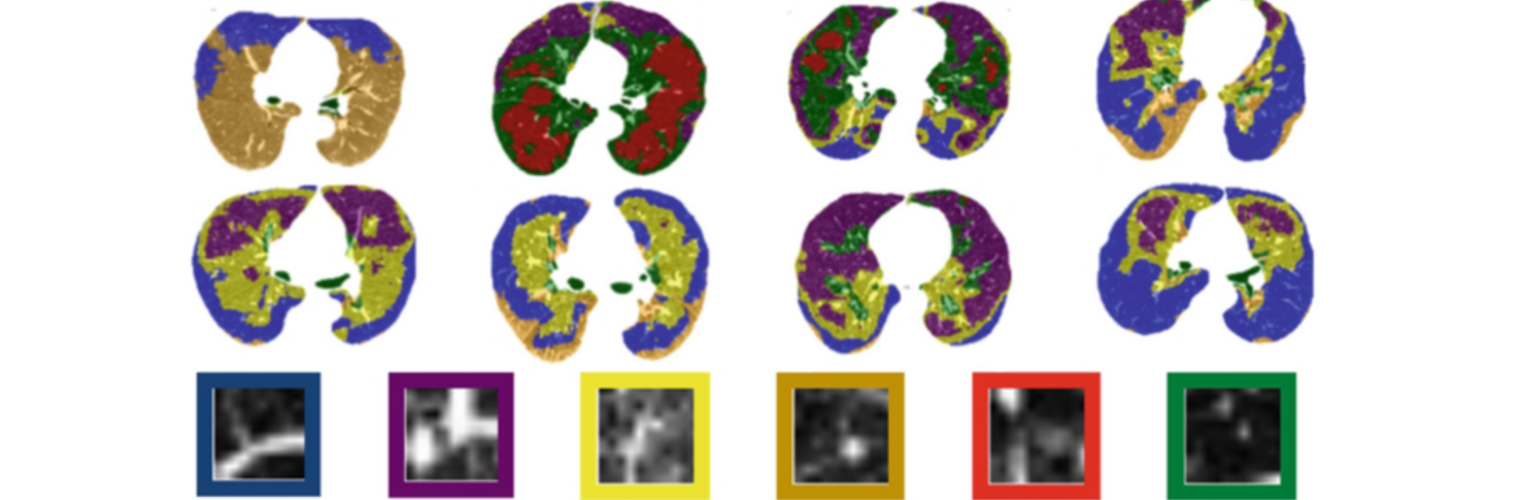
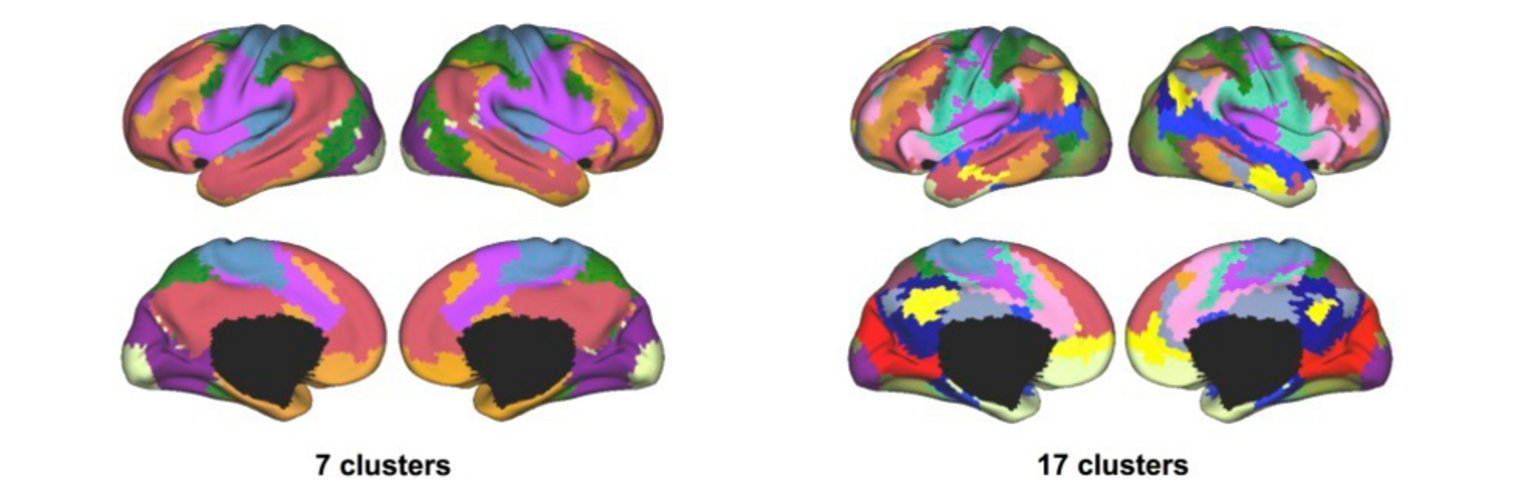
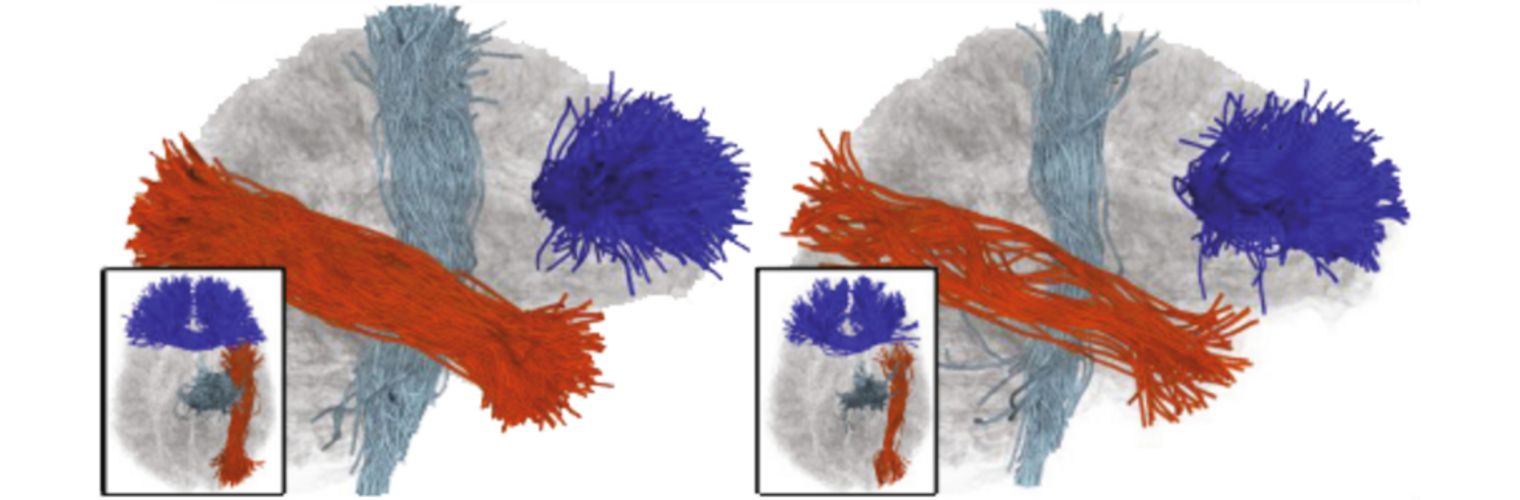
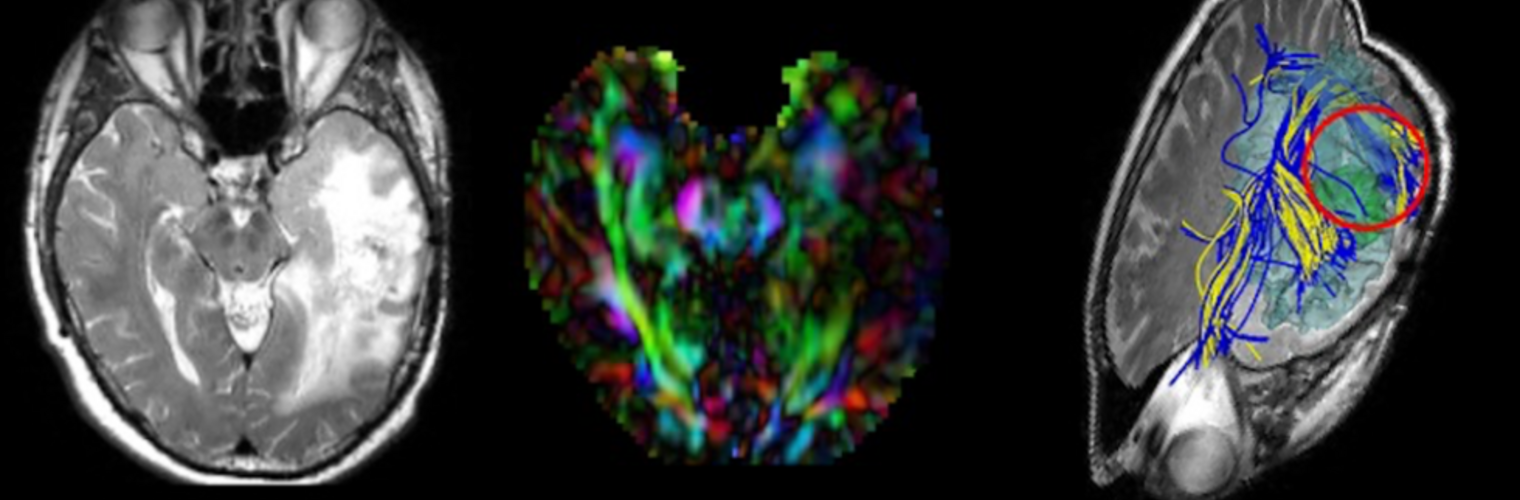
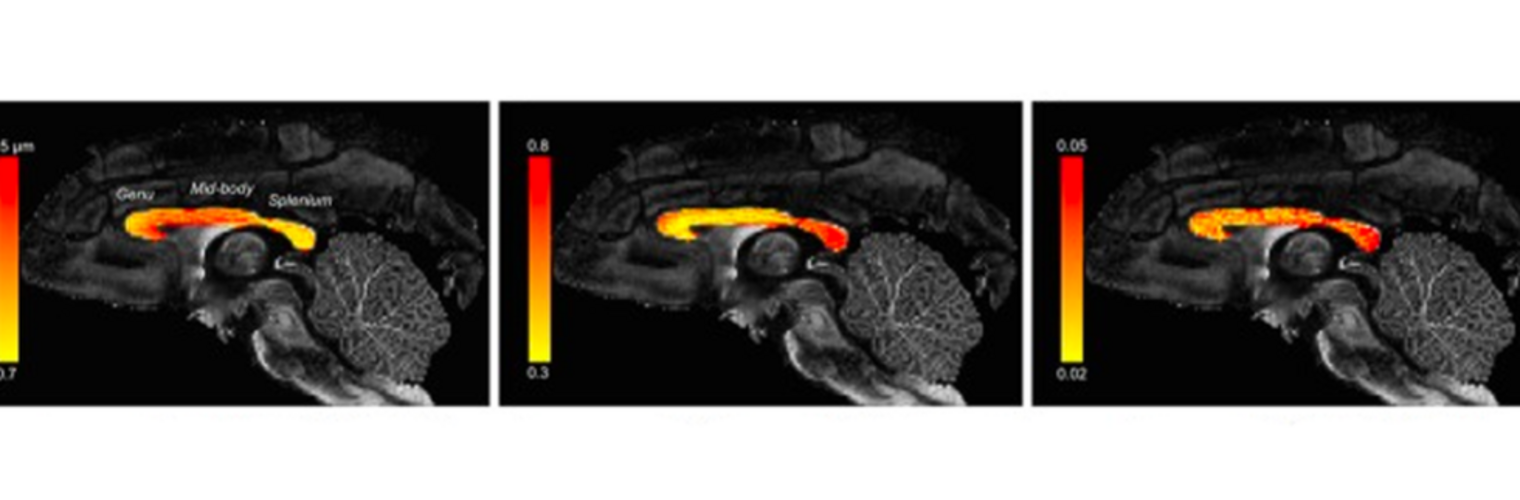
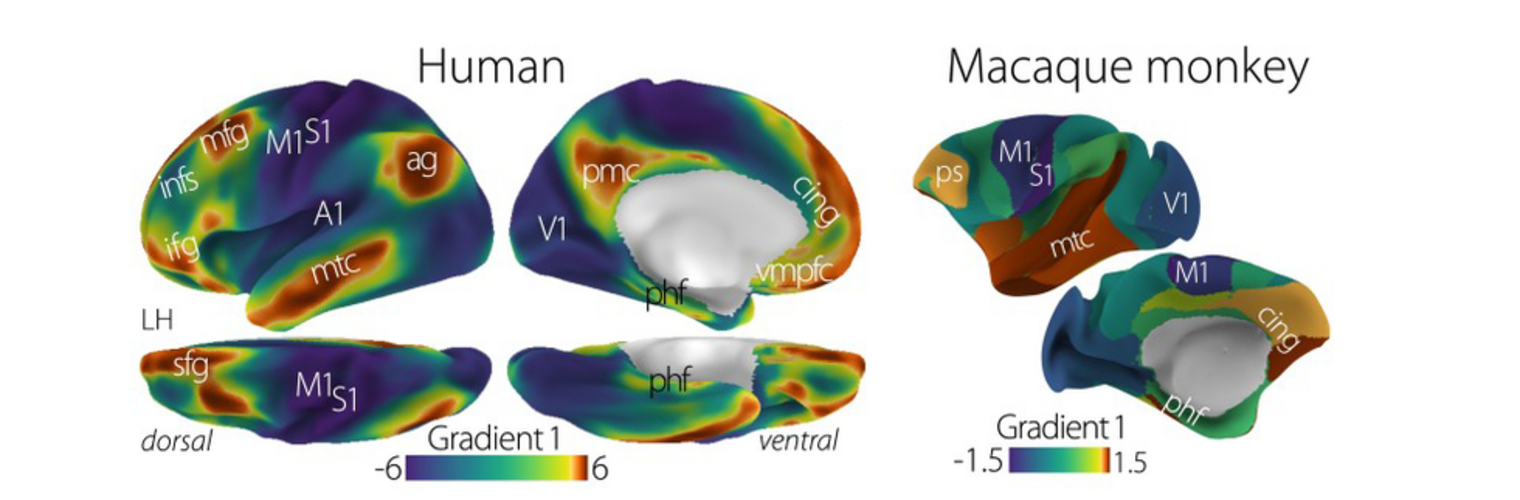
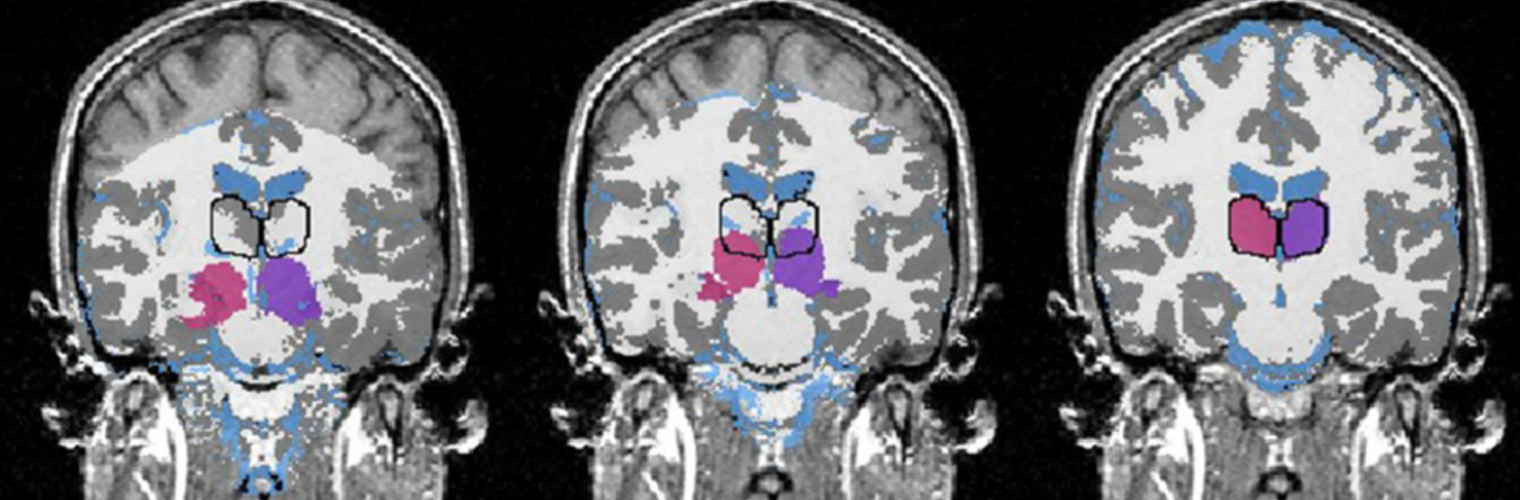
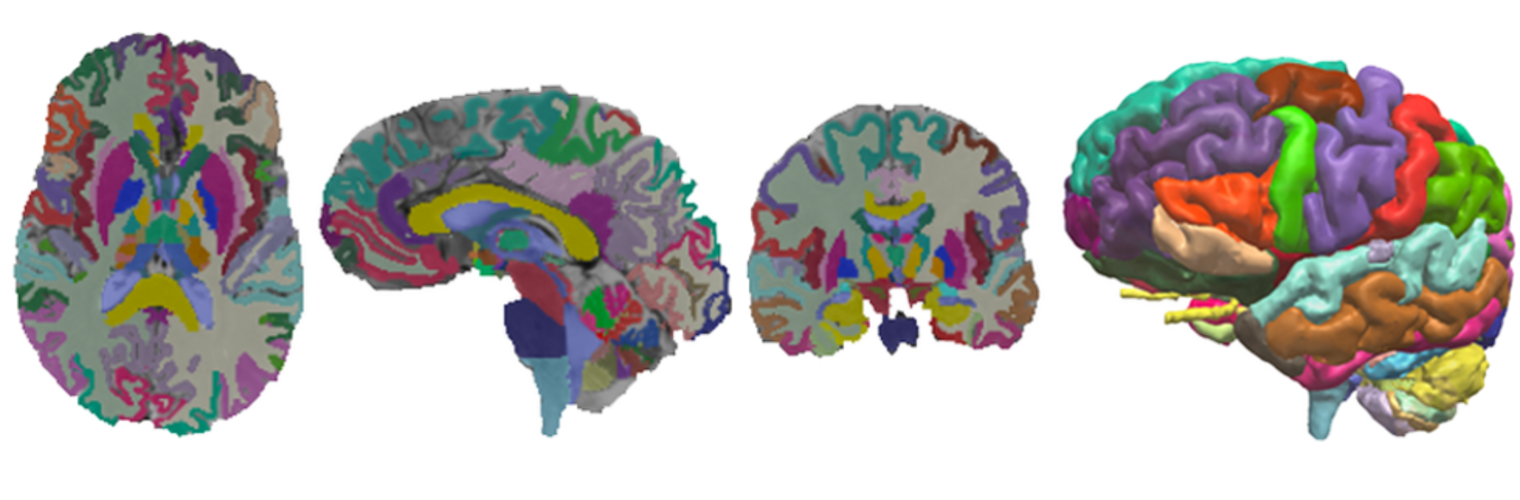
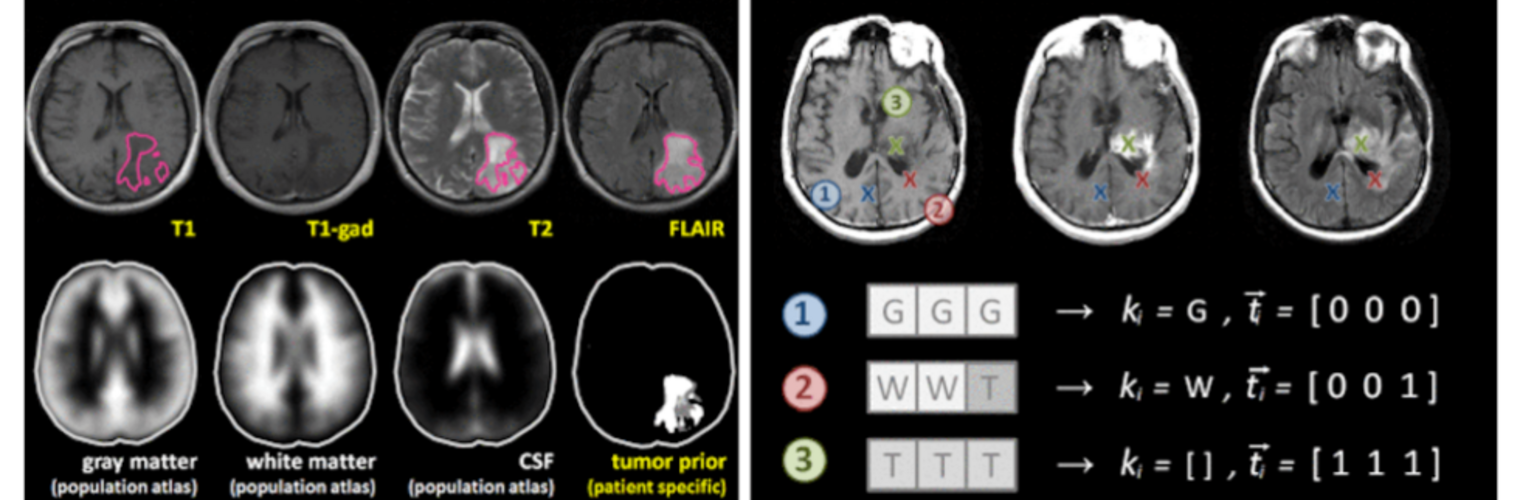
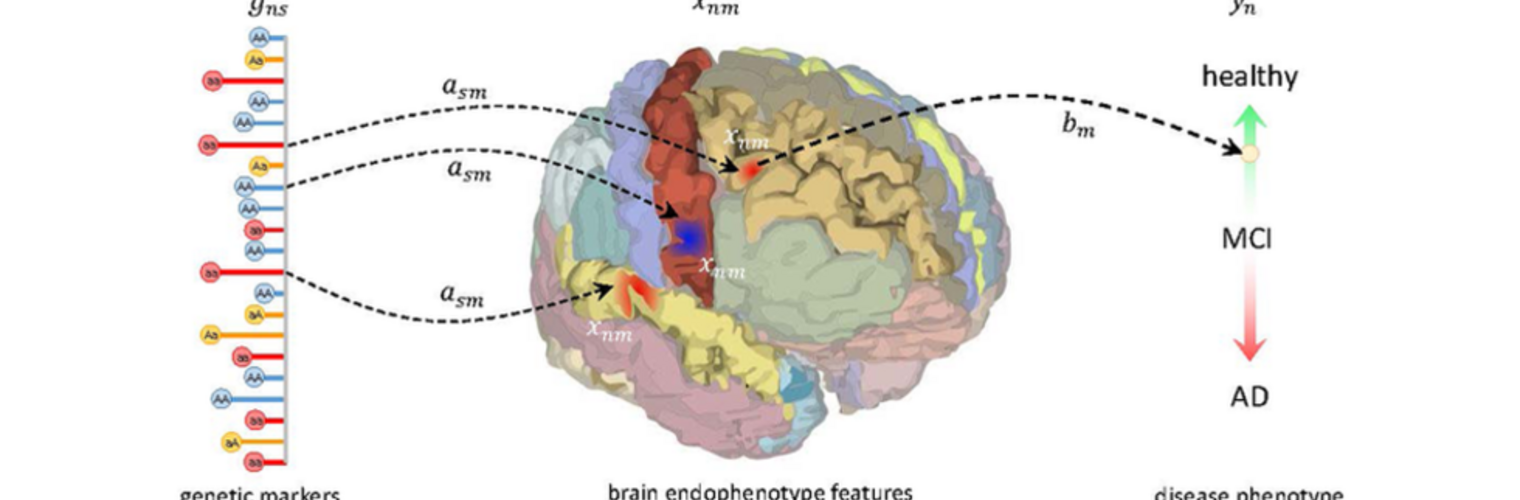
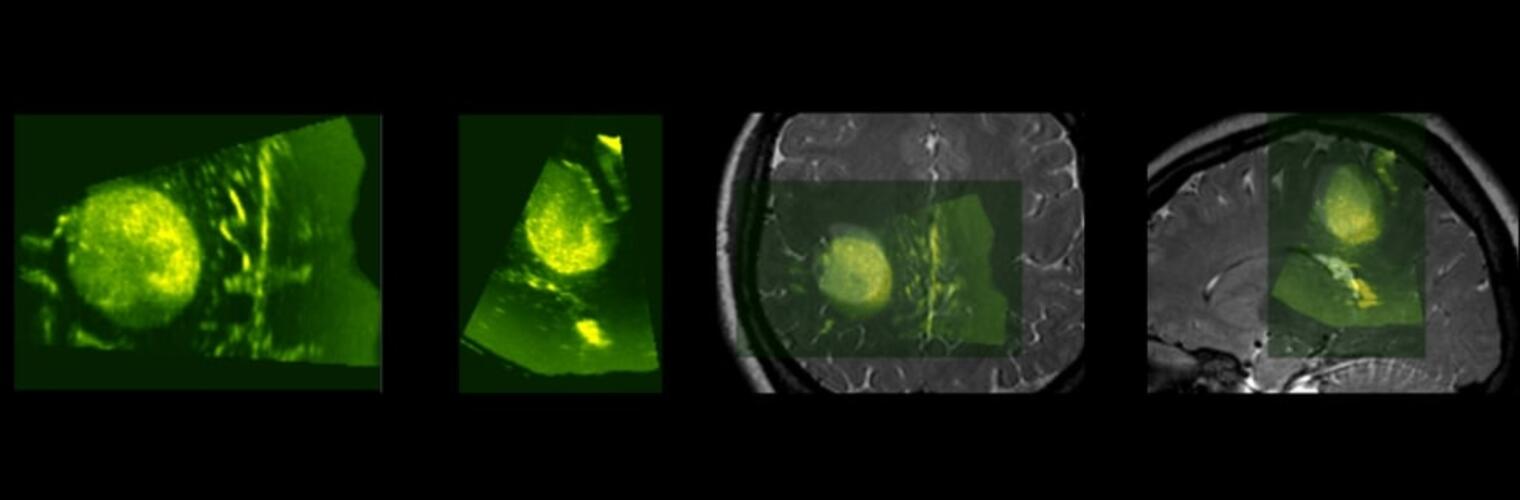
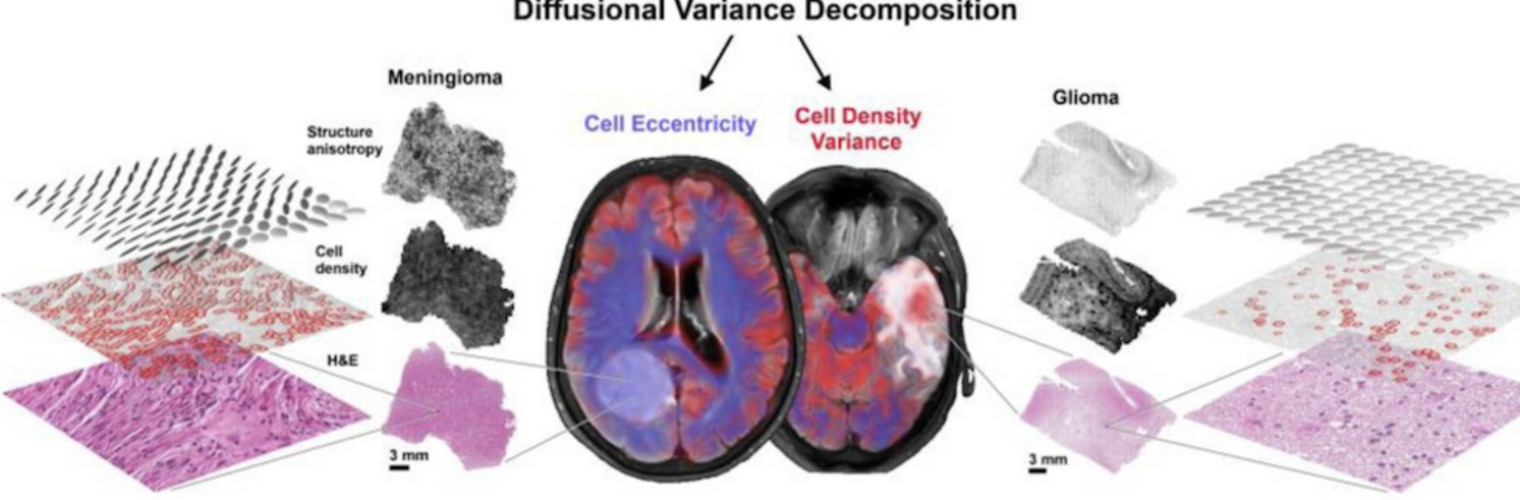
Depression in Parkinson disease (PD) is common, is disabling and responds poorly to standard antidepressants. Motivational symptoms of depression are particularly prevalent in PD and emerge with loss of dopaminergic innervation of the striatum. Optimizing dopaminergic treatment for PD can improve depressive symptoms. However, the differential effect of antiparkinsonian medication on symptom dimensions of depression is not known. Using data from a large (n = 412) longitudinal study of patients with newly diagnosed PD followed over 5 years, we investigated whether there are dissociable effects of dopaminergic medications on different depression symptom dimensions in PD. Previously validated 'motivation' and 'depression' dimensions were derived from the 15-item geriatric depression scale. Dopaminergic neurodegeneration was measured using repeated striatal dopamine transporter imaging. We identified dissociable associations between dopaminergic medications and different dimensions of depression in PD. Dopamine agonists were shown to be effective for treatment of motivational symptoms of depression. In contrast, monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors improved both depressive and motivation symptoms, albeit the latter effect is attenuated in patients with more severe striatal dopaminergic neurodegeneration.
Neuroimage Analysis Center
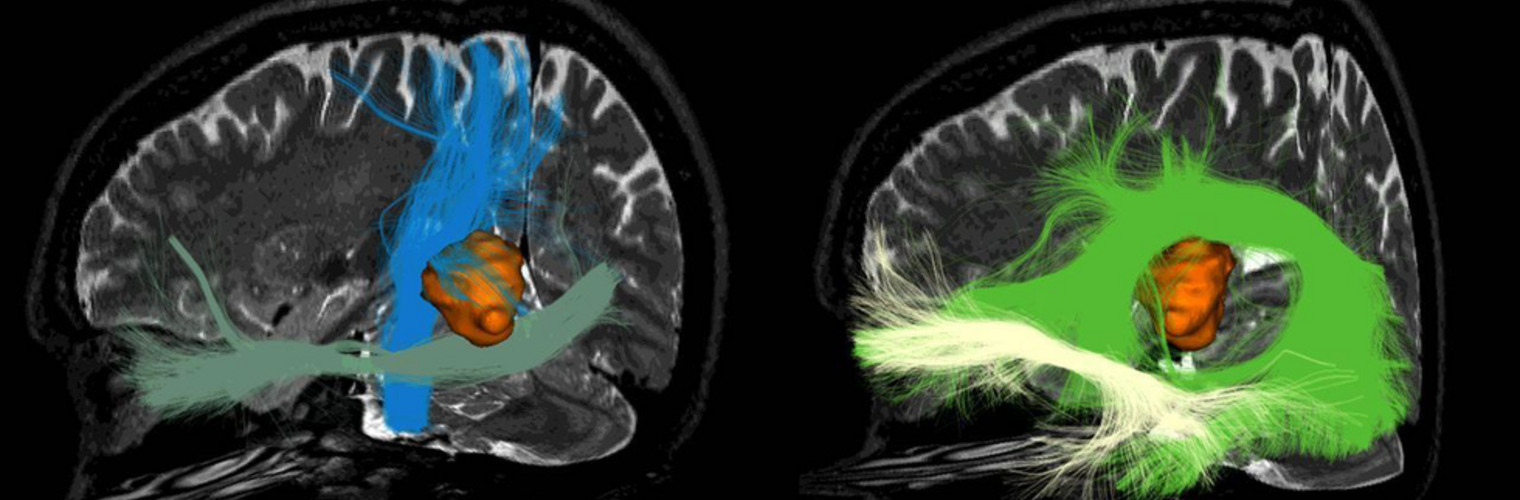
The Neuroimaging Analysis Center is a research and technology center with the mission of advancing the role of neuroimaging in health care. The ability to access huge cohorts of patient medical records and radiology data, the emergence of ever-more detailed imaging modalities, and the availability of unprecedented computer processing power marks the possibility for a new era in neuroimaging, disease understanding, and patient treatment. We are excited to present a national resource center with the goal of finding new ways of extracting disease characteristics from advanced imaging and computation, and to make these methods available to the larger medical community through a proven methodology of world-class research, open-source software, and extensive collaboration.
Our Sponsor

The NAC is a Biomedical Technology Resource Center supported by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) (P41 EB015902). It was supported by the National Center for Research Resources (NCRR) (P41 RR13218) through December 2011.
Contact the Center Directors
|
|
Carl-Fredrik Westin, PhD Laboratory of Mathematics in Imaging Brigham and Women's Hospital 1249 Boylston St., Room 240 Boston, MA 02215 Phone: +1 617 525-6209 E-mail: westin at bwh.harvard.edu |
|
|
|
Ron Kikinis, MD Surgical Planning Laboratory Brigham and Women's Hospital 75 Francis St, L1 Room 050 Boston, MA 02115 Phone: +1 617 732-7389 E-mail: kikinis at bwh.harvard.edu |