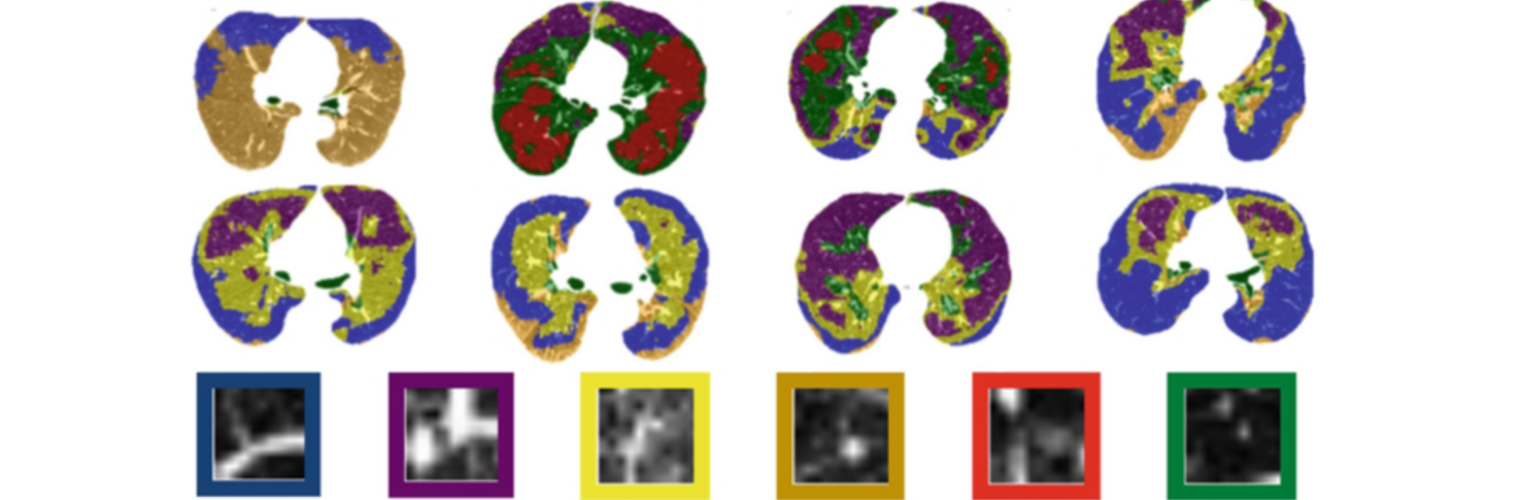
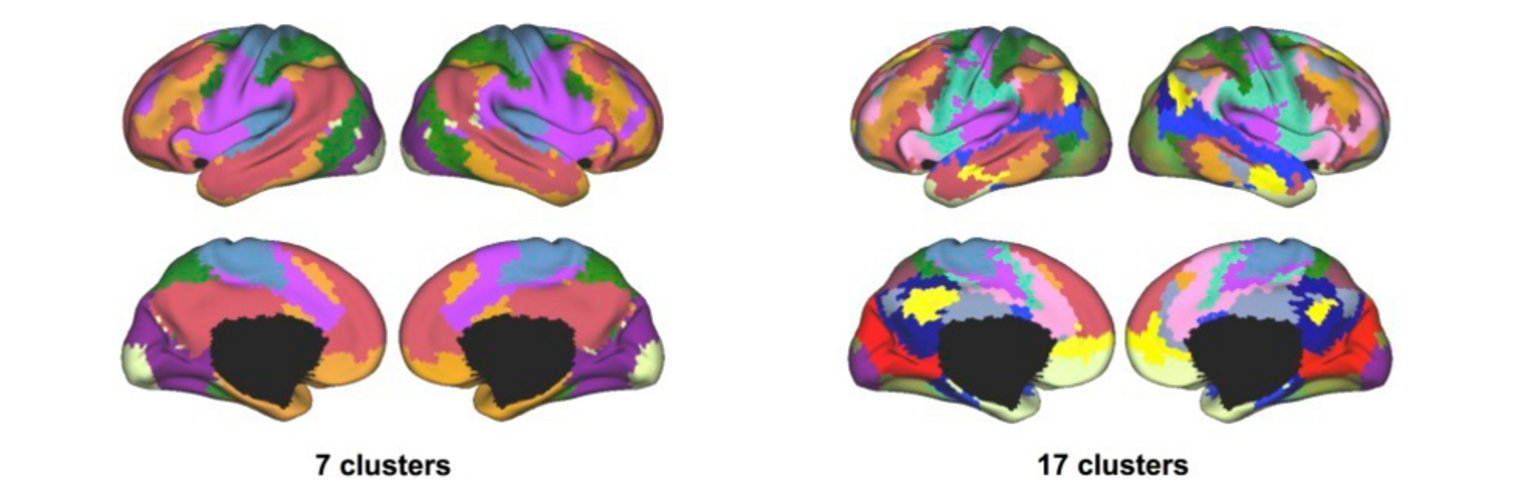
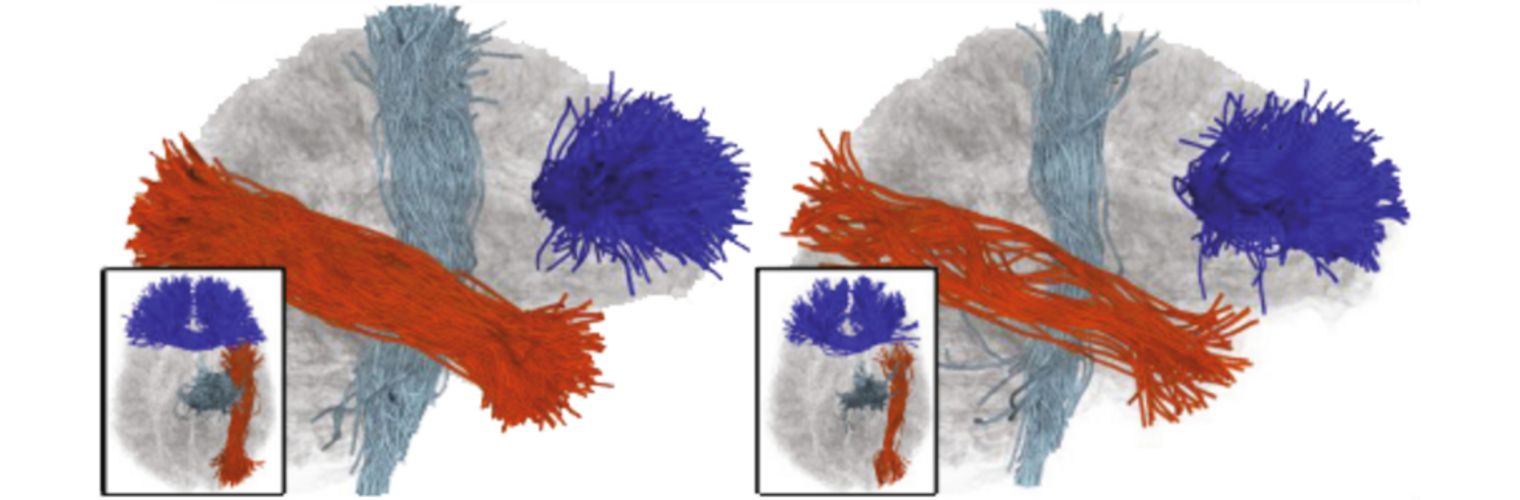
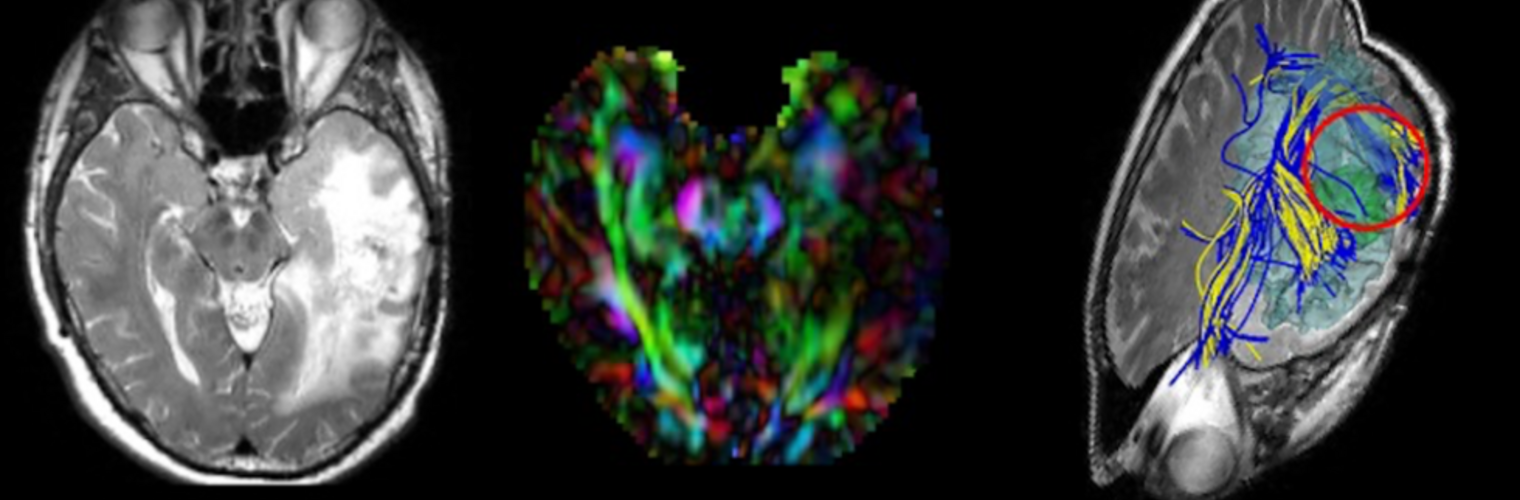
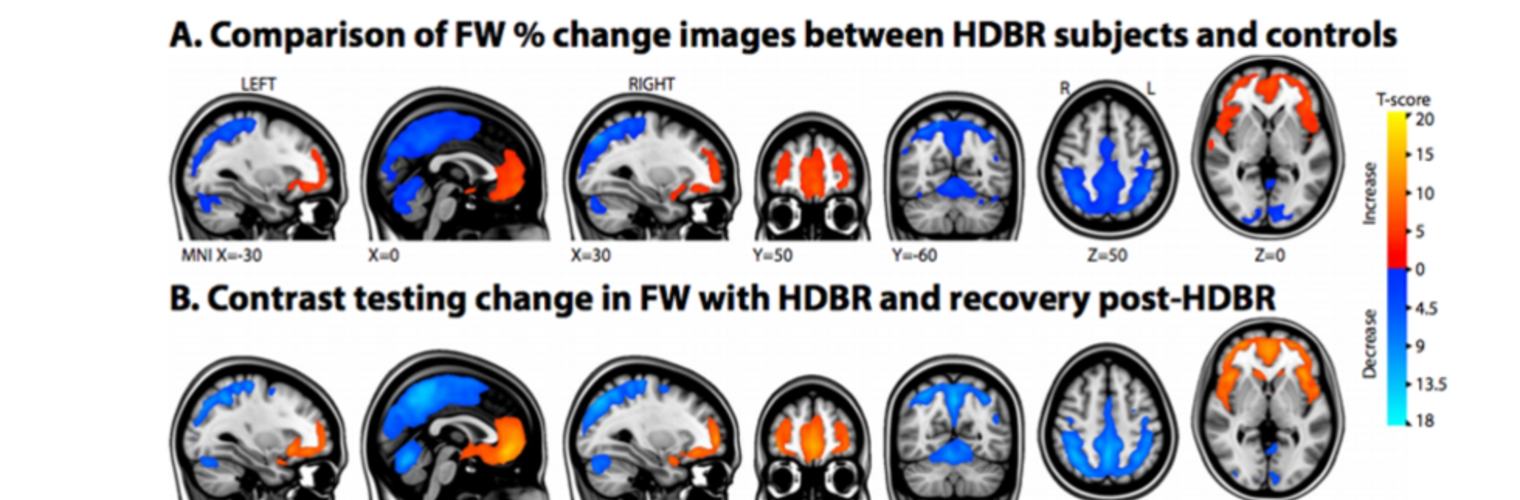
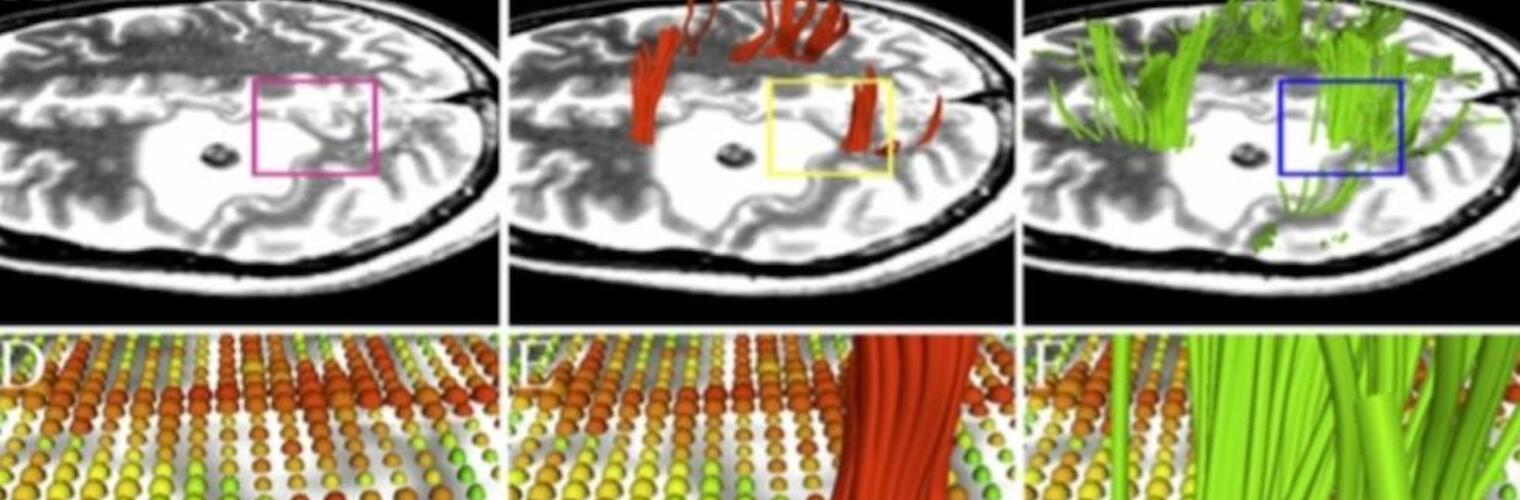
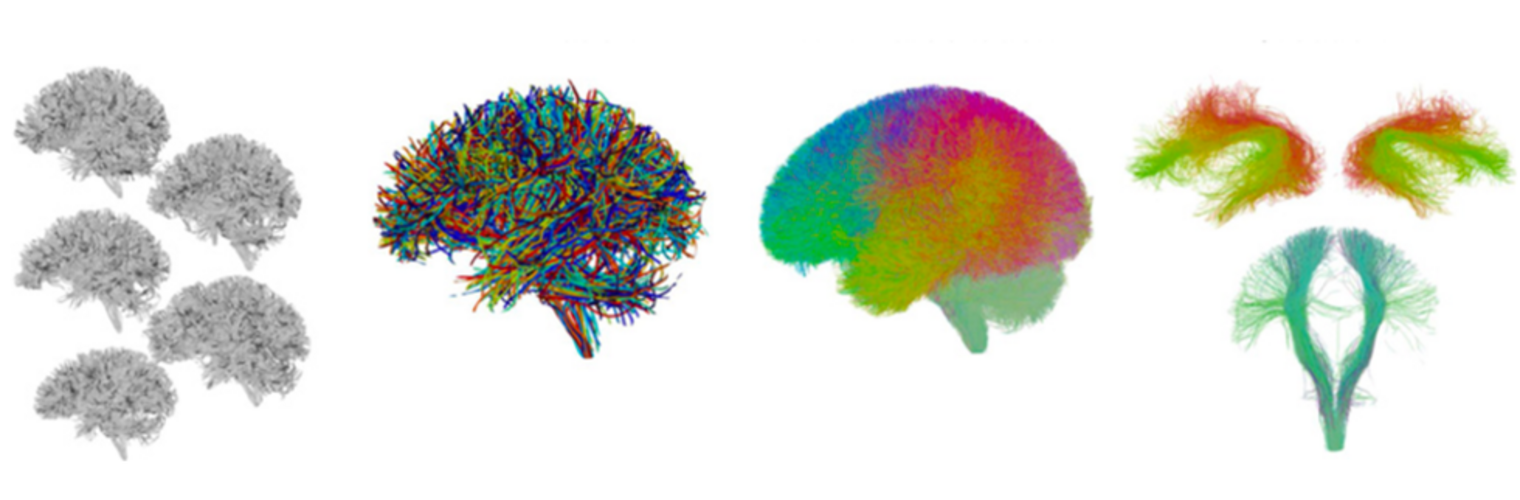
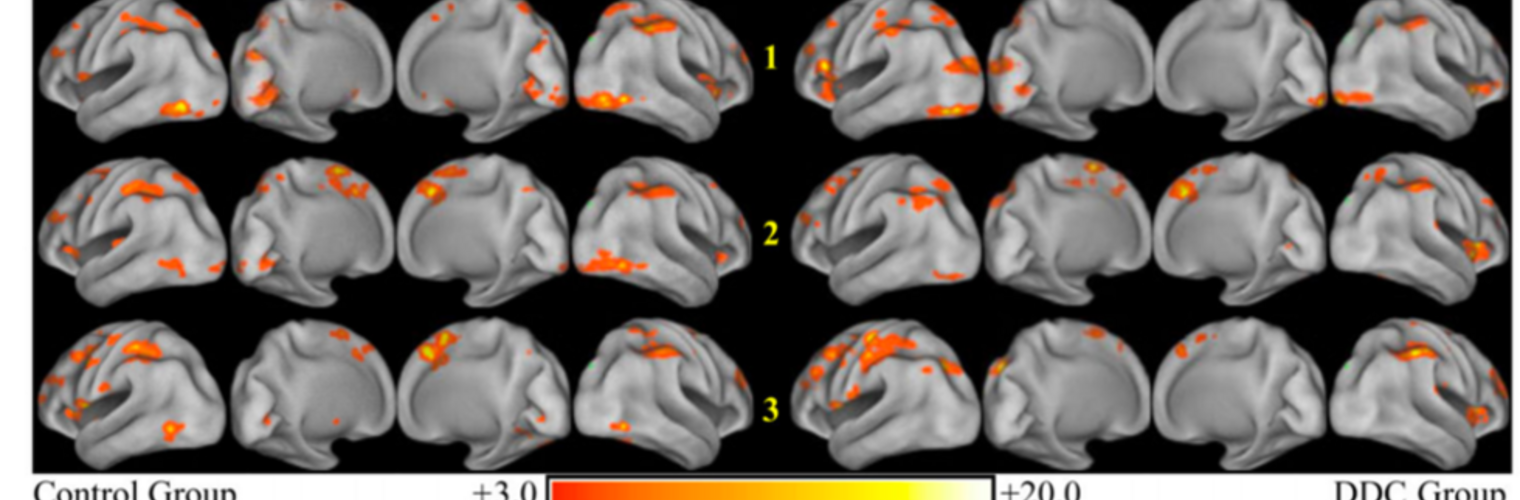
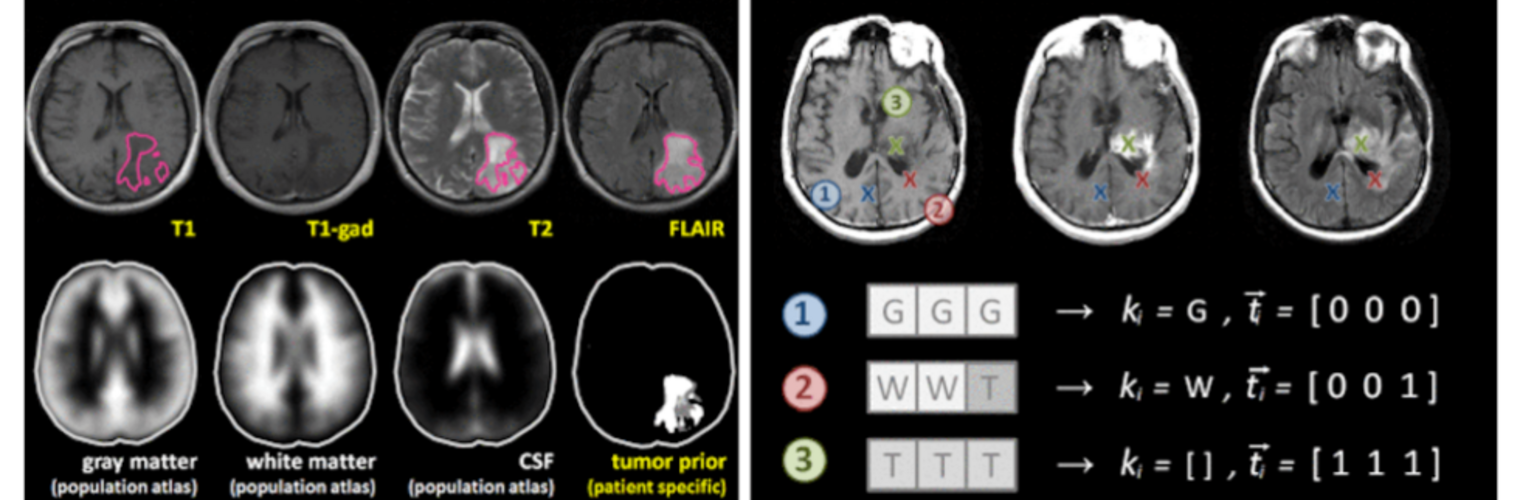
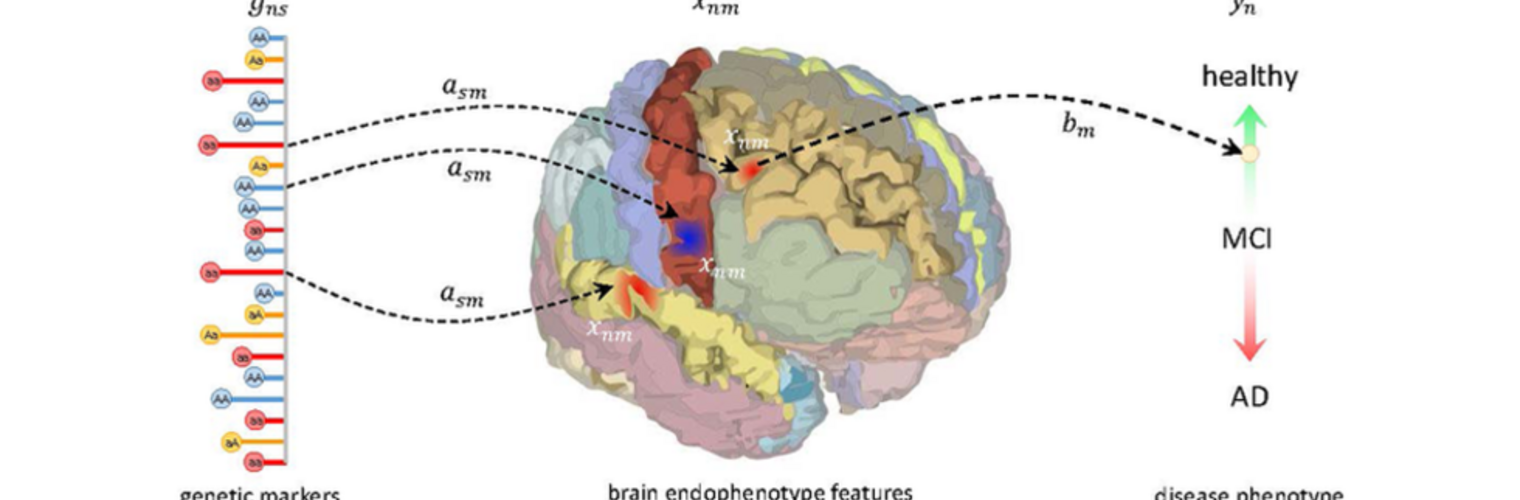
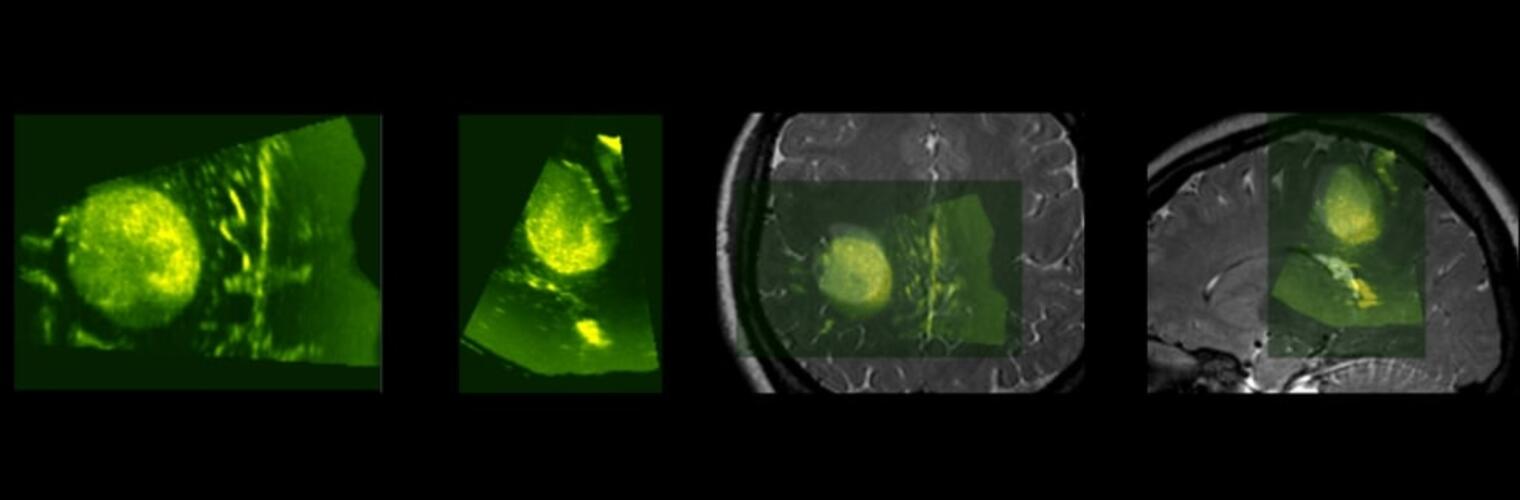
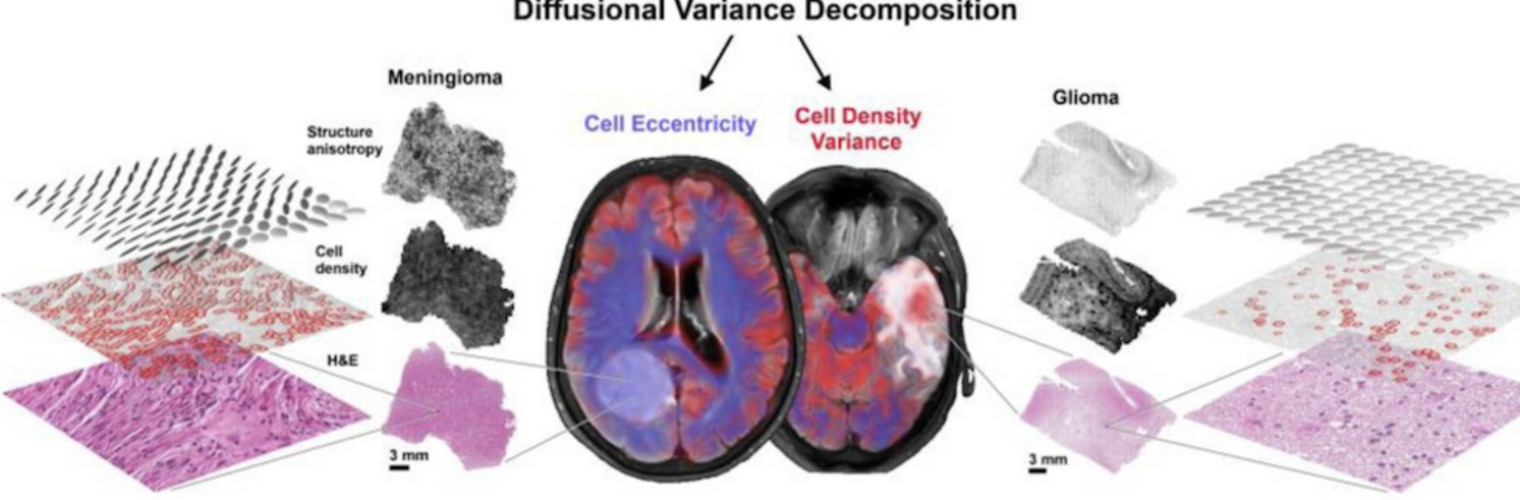
Neuroimage Analysis Center
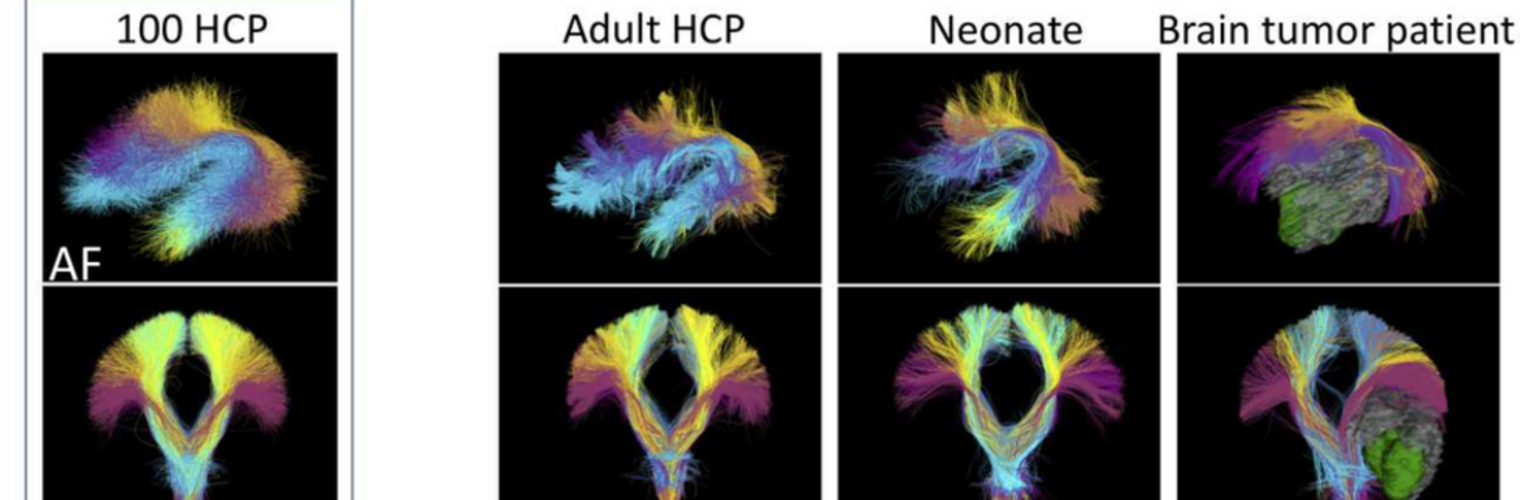
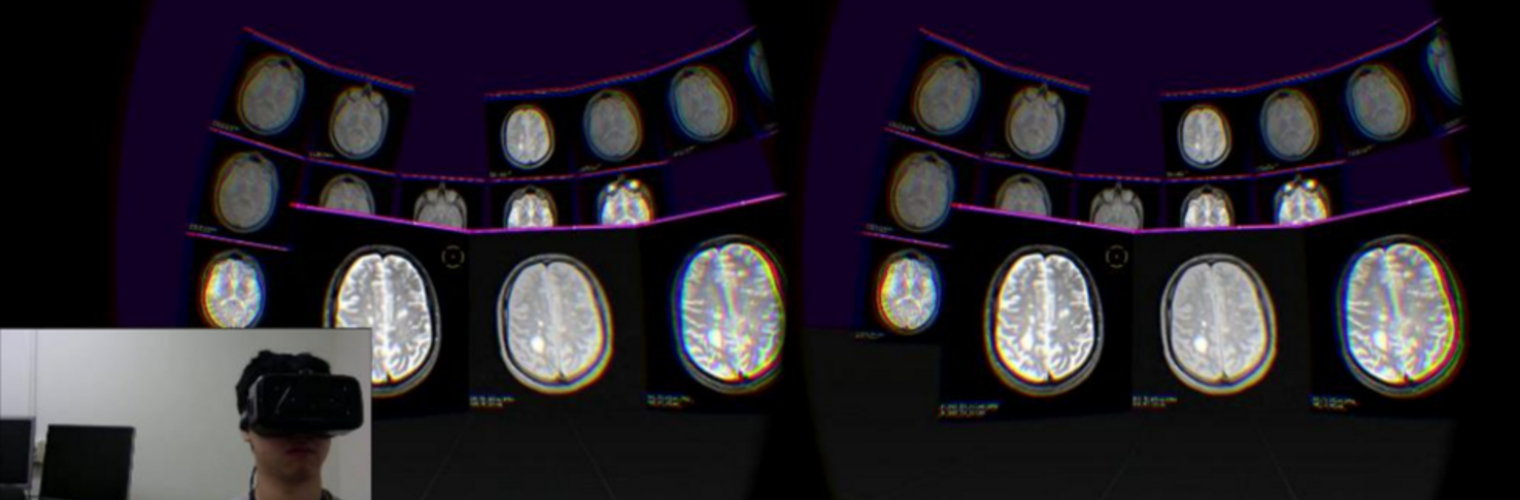
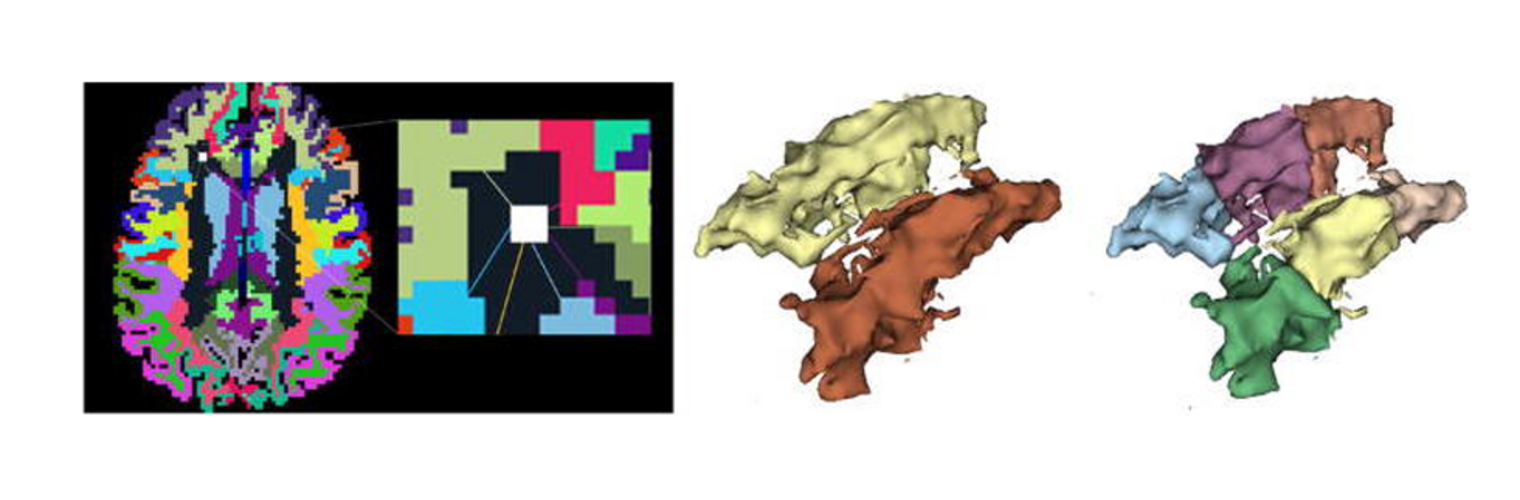
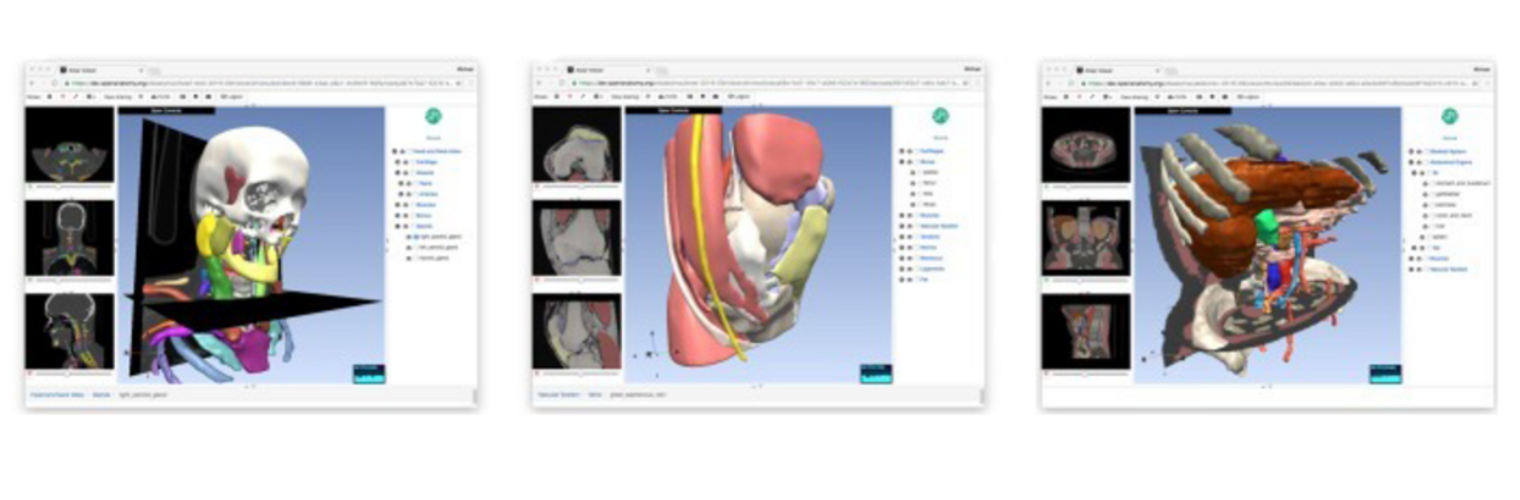
The Neuroimaging Analysis Center is a research and technology center with the mission of advancing the role of neuroimaging in health care. The ability to access huge cohorts of patient medical records and radiology data, the emergence of ever-more detailed imaging modalities, and the availability of unprecedented computer processing power marks the possibility for a new era in neuroimaging, disease understanding, and patient treatment. We are excited to present a national resource center with the goal of finding new ways of extracting disease characteristics from advanced imaging and computation, and to make these methods available to the larger medical community through a proven methodology of world-class research, open-source software, and extensive collaboration.
Our Sponsor

The NAC is a Biomedical Technology Resource Center supported by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) (P41 EB015902). It was supported by the National Center for Research Resources (NCRR) (P41 RR13218) through December 2011.
Contact the Center Directors
|
|
Carl-Fredrik Westin, PhD Laboratory of Mathematics in Imaging Brigham and Women's Hospital 1249 Boylston St., Room 240 Boston, MA 02215 Phone: +1 617 525-6209 E-mail: westin at bwh.harvard.edu |
|
|
|
Ron Kikinis, MD Surgical Planning Laboratory Brigham and Women's Hospital 75 Francis St, L1 Room 050 Boston, MA 02115 Phone: +1 617 732-7389 E-mail: kikinis at bwh.harvard.edu |